CCSI contributes to the economy with 5.3% of the total European GVA (Gross Value Added) and employs more than 12 million people in the EU, 7.5% of the European workforce. In 2022, the EU recognised the relevance of CCSI for Europe's economic and social development by launching a new EIT KIC related to them. CCRE-S3 will be a counterpart of this initiative funded by Horizon Europe, bridging it with Smart Specialisation and macro-regional strategies in the frame of the European Territorial Cooperation.
To this end, CCRE-S3 will stimulate new insights and opportunities related to cultural and creative experiences for local communities and residents through public-private investments involving CCSI-related groups of professionals that use, apply and implement new technologies. Also, we use Digital Innovation Hubs as a meeting point to unify outlooks for promoting new models of CCSI based on user experience, circular business models and co-creation and co-innovation paradigms.
Year established: 2020
An overall challenge is the valorisation of the common characteristics of CCSI and the establishment of an open discovery process to identify strategic investments.
Some examples of challenges when investing in innovative solutions for achieving sustainability and social resilience are:
The following specific objectives will demonstrate the transformative nature of the CCRE:
Modernising CCSI, empowering local communities, sustainable lifestyle, spill-over effects, human-centred design, multi-stakeholder approach, macro-regional strategies.
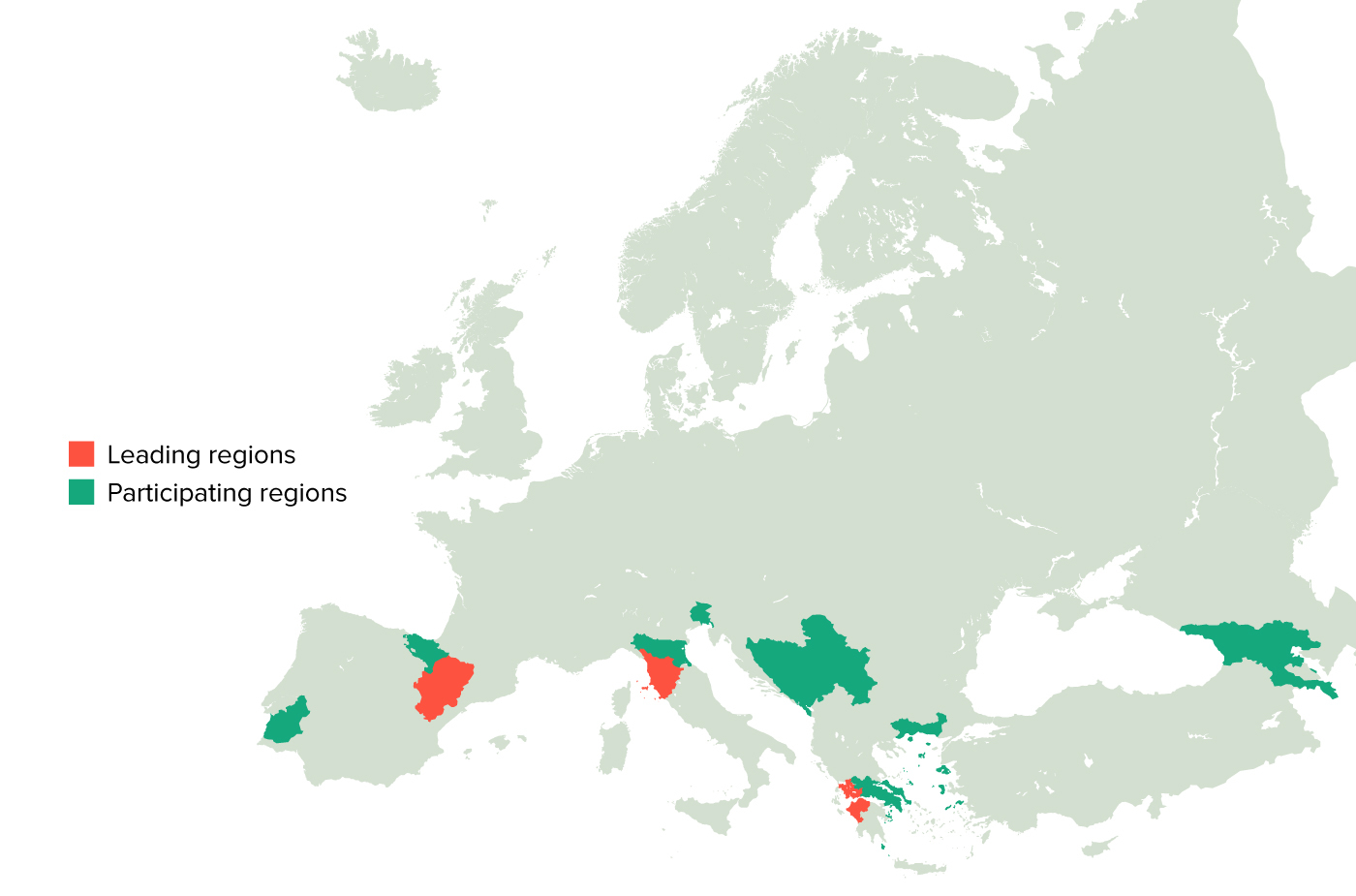
Conference of Peripheral Maritime Regions (CPMR), EU Strategy for the Adriatic and Ionian Region (EUSAIR), Aragon Region (ES), Tuscany Region (IT), Western Greece Region (EL)
Intergroup event with RICC and the ERRIN CCSI cluster.