Climate Change threatens European Union Security and Defence

date: 02/07/2022
See also: Website
Natural hazards and climate change may significantly damage military assets. One of many past examples is the 2019 Midwest flood that hit Offutt Air Force Base in the United States, causing flooding of the runway, electrical and water pump stations, malfunctioning of security systems, and recovery costs of about US$650 million.
Damaged and inaccessible facilities, equipment and supplies, and the disruption of normal functioning are some of the direct impacts that may be observed following a natural hazard impact on a military installation. As important are the indirect impacts resulting from the dependency of military installations on the uninterrupted provision of civilian services, such as energy, water, and telecommunications which – in turn – can also be affected by natural hazards. Such utilities, which often extend over vast areas, are potentially exposed to even more climate change impacts.
As climate change impacts become more evident, it has never been more urgent to reduce GHG emissions and to increase the resilience of the military, including of defence-related critical infrastructure. A proactive approach to building climate resilience into EU military installations, capabilities and investment cycles is required to ensure continuity and operational effectiveness under adverse conditions, avert higher costs, and avoid mission failure with potential repercussions on national and EU security.
This JRC study provides an overview of how natural hazards and climate change increase the potential for disruption, loss or damage in the military sector by using historical case studies that exemplify the potential for negative impacts. It also highlights current gaps and barriers for achieving effective climate change management related to available policy, knowledge, methods and tools, as well as best practices.
In an attempt to help EU stakeholders to reduce risks and strengthen resilience, the JRC study discusses natural hazard specific solutions and proposes short-, medium- and long-term measures at European scale.
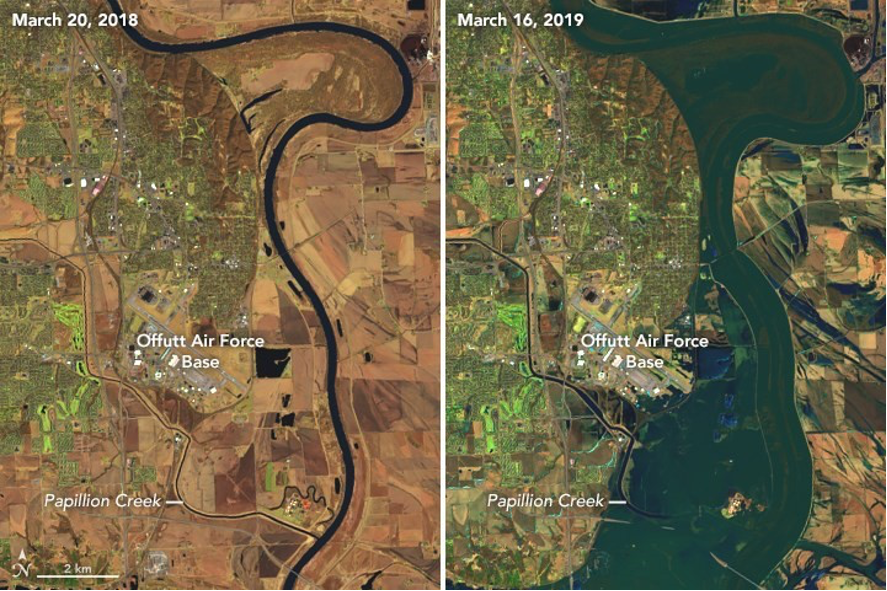
Figure 1. False-colour images from the Landsat 8 satellite, showing the Platte and Missouri River confluence, where Offutt Air Force Base is located, before (20 March 2018) and during the flood (16 March 2019). Source: J. Stevens/NASA
