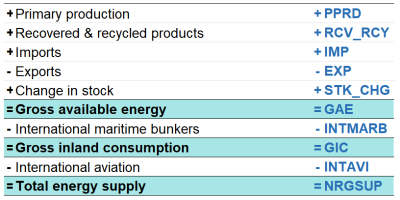
Glossary:Total energy supply
Total energy supply means the overall supply of energy for all activities on the territory of the country, but excluding international aviation and maritime bunkers. It includes energy needs for energy transformation (including generating electricity from combustible fuels), support operations of the energy sector itself, transmission and distribution losses, final energy consumption (industry, transport, households, services, agriculture, ...) and the use of fossil fuel products for non-energy purposes (e.g. in the chemical industry). It excludes international aviation and maritime bunkers, but it might include other fuels purchased within the country that are used elsewhere (e.g. “fuel tourism” in the case of road transport).
This aggregate reflects on the recommendations in IRES for calculation of key aggregates of energy balances. This aggregate is calculated using the following formula:
Total energy supply = Primary production + Recovered & Recycled products + Imports – Export + Stock changes – International maritime bunkers – International aviation
Total energy supply for the total of all products (fuels) is one of the key aggregates in energy balances and represents the quantity of energy necessary to satisfy domestic energy demands. Its interpretation for individual products (fuels) is varying and needs to take into consideration other parts of energy balances. For secondary products, which are produced as transformation output in the middle block of energy balances, the Total energy supply can be negative as it reflects only on the trade and stock changes.