Green ICT - digital devices in households
Do people make green choices with their IT equipment?
Data extracted in June 2023
Planned article update: June 2025
Highlights
In 2022, 10 % of people in the EU recycled their old phone when replacing it, while 17 % gave or sold it to someone else. Meanwhile, almost half simply kept the old device in their household.
In 2022, 13 % of people in the EU recycled their old desktop computer when replacing it, with the highest numbers reported in Sweden (29 %) and the Netherlands (27 %).
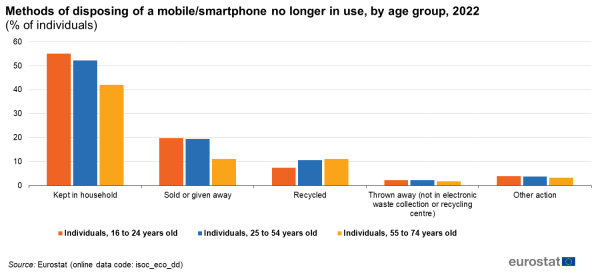
At 11 %, more people in the EU aged 55-74 recycled their old phones in 2022 than those aged 16-24 (7 %). Meanwhile, more young people (20 %) sold or gave away their old device, compared with 11 % for the age group 55-74.
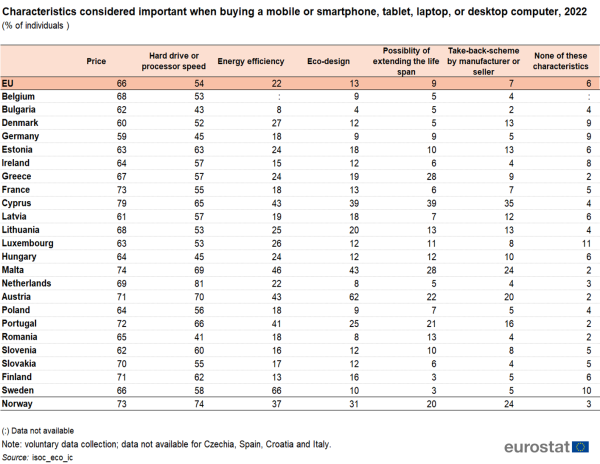
In 2022, 13 % of people in the EU considered the eco-design of IT equipment an important characteristic in their purchasing decision. The highest numbers were reported in Austria (62 %) and Malta (43 %).
This article presents recent statistical data on several different aspects of the digital economy and society in the European Union (EU), focusing on the availability of information and communication technologies (ICTs) and their use by individuals and within households.
The growing use of ICT equipment and the speed at which new devices with more advanced features become available result in a growing amount of waste from old devices, such as laptops, tablets, mobile phones, smartphones and desktop computers. This raises the question of what happens to ICT devices that are no longer in use. There are environmentally friendly ways of disposing of the unused devices, such as disposing of them in a recycling center or by giving them a second life with another user, rather than simply throwing them away or just storing them in a drawer.
Full article
Recycling digital devices
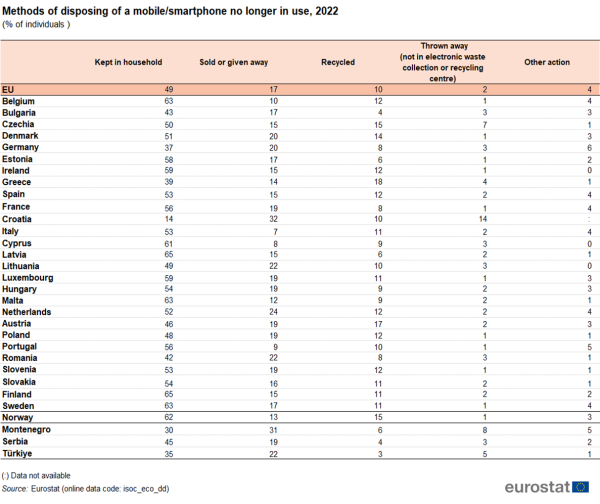
Old mobile phones/smartphones: almost half remain at home, 10 % recycled
In 2022, almost half of EU individuals aged between 16 and 74 simply kept their old mobile phone or smartphone in their household. Around 17 % gave or sold the device to someone else, 10 % recycled it, and 2 % threw it away without recycling.
Greece (18 %) and Austria (17 %) reported the highest rates of people who recycled their old mobile or smartphone in 2022. Croatia (32 %) and the Netherlands (24 %) reported the highest shares of people who gave or sold their old phone to someone else.
(% of individuals aged 16 to 74)
Source: Eurostat (isoc_eco_dd)
At 11 %, more individuals aged between 55 and 74 tended to recycle their old phones than young people between 16 and 24 years (7 %). Meanwhile, more individuals aged between 16 and 24 gave or sold their old device to someone else - 20 % compared with 11 % for the age group 55-74.
(% of individuals aged 16 to 74)
Source: Eurostat (isoc_eco_dd)
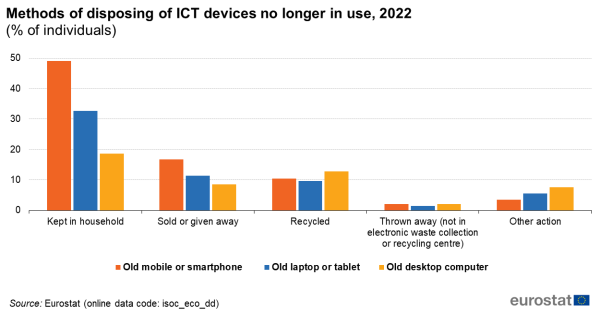
Laptops and tablets: one third remain in the household, 10 % recycled
The recycling rate for laptops and tablets was also 10 % in 2022, compared with 33 % of people who still had the device at home, 11 % who gave or sold it to someone else, and 1 % who threw it away.
The highest rate of people who recycled their old laptop or tablet in 2022 was observed in Sweden and Finland (both 18 %). Croatia (35 %) and France (15 %) reported the highest numbers of people who gave or sold their old laptop or tablet to someone else.
13 % of desktop computers recycled, about one fifth stay in the home
The recycling rate for desktop computers was slightly higher at 13 % in 2022. Meanwhile 19 % still kept the device in their household, 8 % gave or sold it to someone else, and 2 % threw it away without recycling.
Sweden had the highest share of people recycling their old desktop computer (29 %), followed by the Netherlands (27 %). The Netherlands (15 %) and Romania (13 %) reported the highest numbers of people who gave or sold their old desktop computer to someone else.
(% of individuals aged 16 to 74)
Source: Eurostat (isoc_eco_dd)
Sustainability as a purchasing motive
Concerning the importance of sustainability aspects in purchasing decisions of IT equipment, it appeared that in 2022, 13 % of EU individuals considered the eco-design of the device (e.g. durable, upgradeable and reparable designs that require fewer materials; environmentally friendly materials used for packaging) an important characteristic. These numbers were highest in Austria (62 %), Malta (43 %) and Cyprus (39 %).
Additional “green” aspects that were considered were the energy efficiency of the device (22 %), the possibility of extending the life span of the device (9 %) and take-back-schemes offered by sellers or manufacturers (7 %).
However, the most important characteristics in purchasing decisions of IT equipment remained the price (66 %) and hardware characteristics such as hard drive or processor speed (54 %).
(% of individuals aged 16 to 74)
Source: Eurostat (isoc_eco_dd)
Source data for tables and graphs
Data sources
The data presented in this article come from Eurostat’s survey on ICT usage in households and by individuals, which is updated on an annual basis to ensure that the data collected remain relevant. While the questions and areas of interest for the surveys change each year to reflect modern ICT use, there is a core section of the survey which aims to provide stable and continued data collection for several key indicators thereby making analyses over time possible. Currently, information about green ICT is collected every two years. In most EU Member States the surveys are carried out in the second quarter of each year asking about activities in the first quarter of the same year.
Within this article, statistics that refer to the whole adult population cover those aged 16 to74 years. The ICT household survey covers households having at least one member in the relevant age group 16 to 74 years old.
Context
In her agenda for Europe, the President of the European Commission outlined a set of priorities for the period 2019-2024. One of these concerns ‘A Europe fit for the digital age’. In February 2020, the European Commission adopted a Communication on Shaping Europe’s digital future (COM(2020) 67 final), which highlights the opportunities that exist around developing new technologies such as artificial intelligence and 5G networks, or exploiting a wealth of potential information from big data. Alongside encouraging businesses to work on developing these new technologies, the strategy also ensures that any new developments are made while ensuring the trust of European citizens (trustworthy technologies, fostering an open and democratic society, enabling a vibrant and sustainable economy, helping to combat climate change and promote a green transition).
Direct access to
See also
Database
- ICT usage in households and by individuals (isoc_i)
- Green ICT (isoc_eco)
Dedicated section
Publications
Methodology
- Digital economy and society - methodology
- ICT usage in households and by individuals (ESMS metadata file — isoc_i)
- A Digital Single Market Strategy for Europe COM(2015) 192 final
- Monitoring the Digital Economy & Society 2016-2021, European Commission, Directorate-General Communications Networks, Content & Technology
- OECD — Internet