Archive:SDG 4 - Quality education (statistical annex)
Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all (statistical annex)
Data extracted in May 2020.
Planned article update: June 2021.
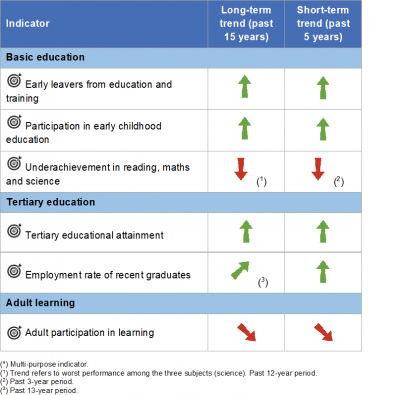
Highlights
This article provides an overview of statistical data on SDG 4 ‘Quality education’ in the European Union (EU). It is based on the set of EU SDG indicators for monitoring of progress towards the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in an EU context.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles, which are based on the Eurostat publication ’Sustainable development in the European Union — Monitoring report - 2020 edition’. This report is the fourth edition of Eurostat’s series of monitoring reports on sustainable development, which provide a quantitative assessment of progress of the EU towards the SDGs in an EU context.
Full article
Early leavers from education and training
This indicator measures the share of the population aged 18 to 24 with at most lower secondary education who were not involved in any education or training during the four weeks preceding the survey. The data stem from the EU Labour Force Survey (EU-LFS).
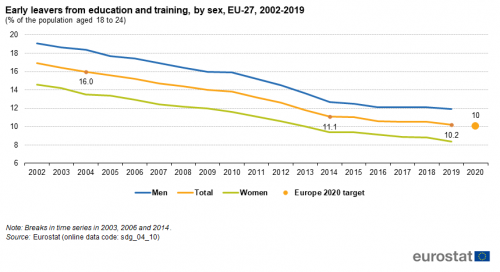
Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_10)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_10)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_10)
Participation in early childhood education
This indicator measures the share of children between the age of four and the starting age of compulsory primary education who participated in early childhood education. Data presented here stem from the joint UIS (UNESCO Institute of Statistics)/OECD/Eurostat (UOE) questionnaires on education statistics, which constitute the core database on education.

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_30)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_30)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_30)
Underachievement in reading, maths and science
This indicator measures the share of 15-year-old students failing to reach level 2 (‘basic skills level’) on the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) scale for the three core school subjects of reading, mathematics and science. The data stem from the PISA study, a triennial international survey that aims to evaluate education systems by testing the skills and knowledge of 15-year-old students.

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_40)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_40)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_40)
Tertiary educational attainment
This indicator measures the share of the population aged 30 to 34 who have successfully completed tertiary studies (for example, at university or a higher technical institution). Tertiary educational attainment refers to ISCED (International Standard Classification of Education) 2011 levels 5–8 for data from 2014 onwards and to ISCED 1997 levels 5–6 for data up to 2013. The indicator is based on the EU Labour Force Survey (EU-LFS).

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_20)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_20)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_20)
Employment rate of recent graduates
The employment rate of recent graduates is defined as the percentage of the population aged 20 to 34 with at least upper-secondary education (ISCED 2011 levels 3 to 8) who are in employment, not in any education and training during the four weeks preceding the survey, and who have successfully completed their highest educational attainment one to three years before the survey. The data stem from the EU Labour Force Survey (EU-LFS).

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_50)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_50)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_50)
Adult participation in learning
Adult participation in learning refers to people aged 25 to 64 who stated they received formal or non-formal education and training in the four weeks preceding the survey (numerator). The denominator consists of the total population of the same age group, excluding those who did not answer the question ‘participation in education and training’. Adult learning covers formal and non-formal learning activities — both general and vocational — undertaken by adults after leaving initial education and training [1]. Data stem from the EU Labour Force Survey (EU-LFS).

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_60)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_60)
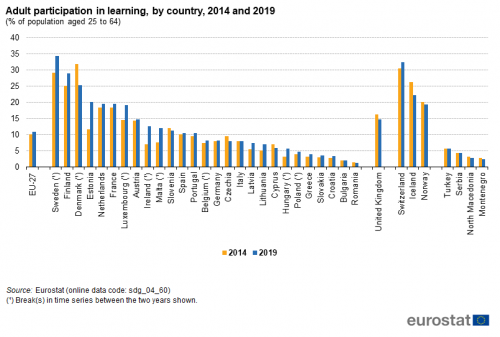
Source: Eurostat (sdg_04_60)
Direct access to
More detailed information on EU SDG indicators for monitoring of progress towards the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), such as indicator relevance, definitions, methodological notes, background and potential linkages, can be found in the introduction of the publication ’Sustainable development in the European Union — Monitoring report - 2020 edition’.
Notes
- ↑ The general definition of adult learning covers formal, non-formal and informal training but the indicator adult participation in learning only covers formal and non-formal education and training. For more information, see: Eurostat, Participation in education and training.