Archive:SDG 5 - Gender equality (statistical annex)
Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls (statistical annex)
Data extracted in May 2020.
Planned article update: June 2021.
Highlights
This article provides an overview of statistical data on SDG 5 ‘Gender equality’ in the European Union (EU). It is based on the set of EU SDG indicators for monitoring of progress towards the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in an EU context.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles, which are based on the Eurostat publication ’Sustainable development in the European Union — Monitoring report - 2020 edition’. This report is the fourth edition of Eurostat’s series of monitoring reports on sustainable development, which provide a quantitative assessment of progress of the EU towards the SDGs in an EU context.
Full article
Physical and sexual violence to women
This indicator is based on the results of a survey by the European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights (FRA). Women were asked whether they had experienced physical and/or sexual violence within the 12 months prior to the interview.
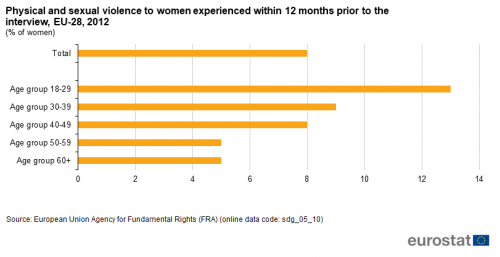
Source: FRA (sdg_05_10)
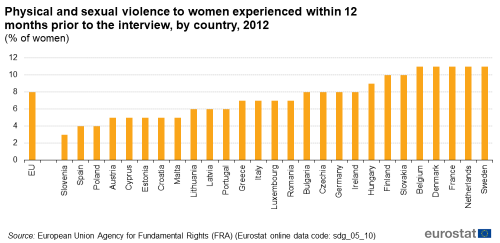
Source: FRA (sdg_05_10)
Gender pay gap in unadjusted form
The gender pay gap in unadjusted form represents the difference between average gross hourly earnings of male paid employees and of female paid employees as a percentage of average gross hourly earnings of male paid employees. The indicator has been defined as unadjusted because it gives an overall picture of gender inequalities in terms of pay and measures a concept which is broader than the concept of equal pay for equal work. The gender pay gap is based on the methodology of the structure of earnings survey (SES), which is carried out every four years.
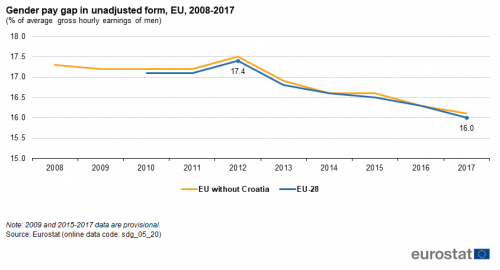
Source: Eurostat (sdg_05_20)
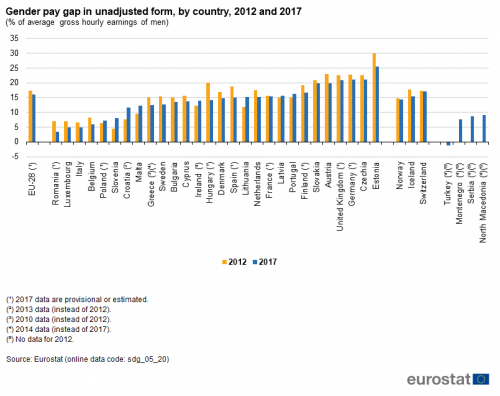
Source: Eurostat (sdg_05_20)
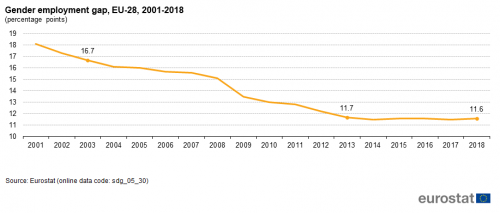
Gender employment gap
The gender employment gap is defined as the difference between the employment rates of men and women aged 20 to 64. The employment rate is calculated by dividing the number of people aged 20 to 64 in employment by the total population of the same age group. The indicator is based on the EU Labour Force Survey (EU-LFS).
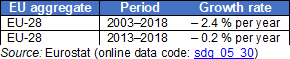
Source: Eurostat (sdg_05_30)

Source: Eurostat (sdg_05_30)
Gender gap for inactive population due to caring responsibilities
The economically inactive population comprises individuals that are not working, not actively seeking work and not available to work even if they have found a job. Therefore, they are neither employed nor unemployed and considered to be outside the labour force. This definition used in the EU Labour Force Survey (EU-LFS) is based on the guidelines of the International Labour Organization.
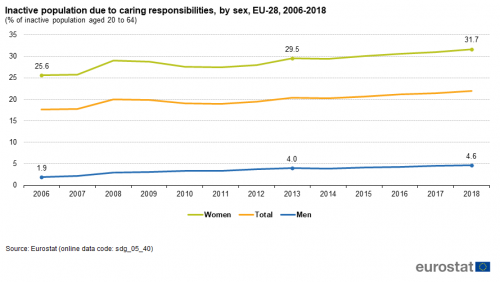
Source: Eurostat (sdg_05_40)
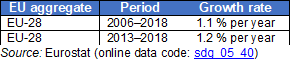
Source: Eurostat (sdg_05_40)
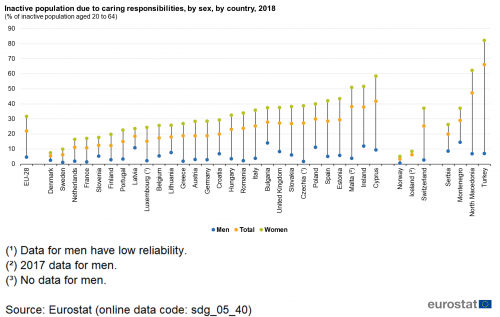
Source: Eurostat (sdg_05_40)
Seats held by women in national parliaments
This indicator refers to the proportion of women in national parliaments in both chambers (lower house and upper house, where relevant). The data stem from the Gender Statistics Database of the European Institute for Gender Equality.
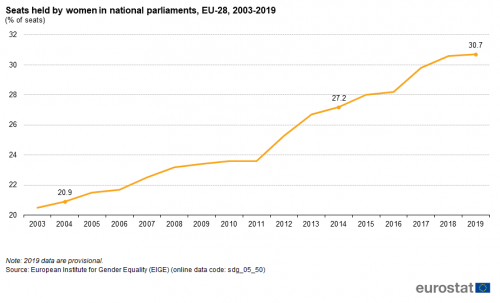
Source: EIGE (sdg_05_50)
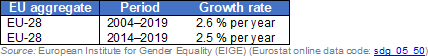
Source: EIGE (sdg_05_50)

Source: EIGE (sdg_05_50)
Positions held by women in senior management
This indicator measures the share of female board members in the largest publicly listed companies. The data presented in this section stem from the Gender Statistics Database of the European Institute for Gender Equality.
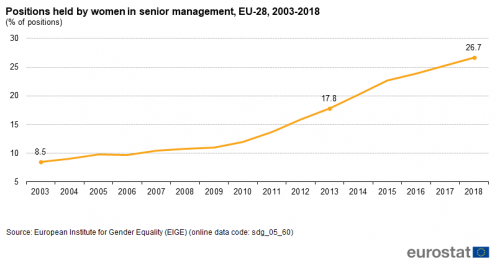
Source: EIGE (sdg_05_60)

Source: EIGE (sdg_05_60)

Source: EIGE (sdg_05_60)
Direct access to
More detailed information on EU SDG indicators for monitoring of progress towards the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), such as indicator relevance, definitions, methodological notes, background and potential linkages, can be found in the introduction of the publication ’Sustainable development in the European Union — Monitoring report - 2020 edition’.