Archive:Farm structure in Spain - 2007 results
- Data from February 2008, most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
This article is part of a series of country-specific essays on the results of the European Union Farm structure survey 2007. It provides a brief but nevertheless comprehensive insight into farm structure in Spain.
The 2007 FSS recorded 1 043 900 agricultural holdings in Spain, which represents a 3.3 % decrease since 2005.
Main statistical findings
Rape and turnip plantations tripled between 2005 and 2007
In 2007, about 939 500 agricultural holdings in Spain had an economic size of at least one European size unit, compared to 959 000 in 2005 (a 2 % reduction).
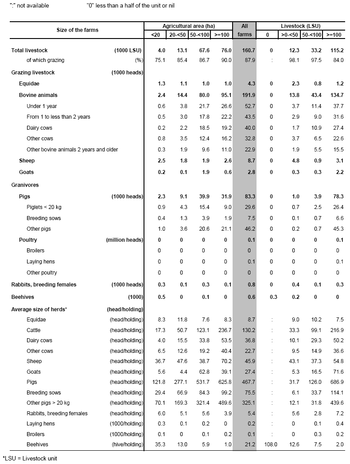
These farms made use of 23.87 million hectares (ha) of utilized agricultural area, (0.5 % more than in 2005), which makes the average size of a holding in Spain 25.4 ha ( compared with 24.8 ha in 2005). See Graph 1 for the distribution of UAA in terms of farm size, while Table 2 describes the size distribution and other characteristics of the agricultural holdings.
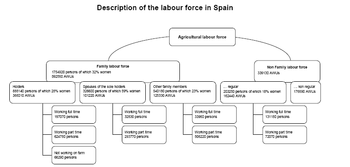
These holdings employed 931 700 annual work units (AWUs), the equivalent of 931 700 people working full time, a decrease of 1.8 % since 2005. The average area per AWU is 25.6 ha (around 0.6 ha more than in 2005). The organization and distribution of the labour force in Spain is described in Graph 2 and Table 1.
The farms contained 14.33 million livestock units (LSU) in 2007, 0.4 % less than in 2005. The distribution of livestock by farm size is shown in Table 4 and Graph 3.
Amongst the 939 500 agricultural holdings in 2007:
- 63 % made use of less than one AWU, while another 11 % made use of two or more AWUs;
- 5 % used less than 2 ha, while 10 % used 50 ha or more;
- 21 % of Spanish farms specialised in olives;
- 19 % were specialists in fruit and citrus fruits;
- 11 % of the holdings specialised in cereals, oil seed and protein crops;
- 8 % of the holdings specialised in vineyards; and
- 7 % specialised in various permanent crops combined;
Amongst the sole holders:
- 28 % were women in 2007;
- 60 % were aged 55 or more and 5 % were younger than 35 years; and
- 26 % had another gainful activity in 2007.
In Spain in 2007, 68 % of the agricultural area was farmed by its owners.
The family labour force represents 64 % of the total labour force - a 3 % decrease from 2005 to 2007.
There was a noticeable increase in the area used for rape and turnip (multiplied by 3), sunflower and other oilseed or fibre plants (+18 %). Details of land use by size of farm are given in Table 3.
The area used for pulses fell by 35 %. The area used for cereals slightly decreased (-1.3 %), but among cereals there were significant differences. The areas used for durum wheat decreased by 21 %; the areas used for grain maize (+11 %), rye (+11 %), oats (+5 %) and barley (+2 %) all increased.
The situation for subsistence farming in Spain is outlined in Table 5.
Data sources and availability
Due to the different coverage of the FSS across Member States, the total number of farms is not comparable between countries. This is why the present analysis, including Tables 1-4 and the graphs focus on holdings of at least one European size unit.
The Spanish National Institute of Statistics (INE) in collaboration with their Provincial Offices and the Regional Statistical Offices of the Basque Country and Catalonia, implemented the survey on the structure of agricultural holdings in Spain. The FSS 2007 was the third survey after the last Agricultural Census in 1999 (AC 1999). The reference period was from October 2006 to September 2007 except in the case of the livestock; here the reference date is the day of the interview (that was conducted between 8 October and 31December).
The holdings targeted by the survey had at least 1 ha of UAA or 0.2 ha of UAA under vegetables, flowers, and ornamental plants, crops under glass, irrigated fruit trees (including citrus) or nurseries, or had, in the AC 1999, one or more livestock units and a Total Gross Margin of at least 0.75 ESU (900 – Euro SGM).
The sampling frame consisted of 1.29 million holdings (that meet the criteria mentioned above), which were taken from the results of the Agriculture Census 1999, subsequently updated with administrative sources.
From the initial population a panel of farms was selected and used for the FSS surveys (2003, 2005 and 2007) with a initial size close to 54 000 holdings. The sample was updated by the "daughter farms" (new farms that are generated when old farms cease their activity).This sample is chosen using a stratified simple random sample and the Bethel algorithm allocation method.
The stratification criteria used were the administrative districts (NUTS II), typology, and 5 size classes defined by economic size, annual working unit, livestock unit, utilised agricultural area and area taken together by arable land, permanent crops and kitchen gardens.
Altogether about 46 490 questionnaires were completed using a face-to-face interview (response rate was 90,8 %). Imputation was used for total and item nonresponse.
Between FSS 2005 and 2007 "maintaining land in good agricultural and environmental conditions" (GAEC) became an agricultural activity and the concerned land has been included in the agricultural area. In Spain it covers close to 250 000 ha, 97% in holdings with at least 1 ESU.
For each activity (`enterprise`) on a farm (for instance wheat, dairy cow or vineyard), a Standard Gross Margin (SGM) is estimated, based on the area (or the number of heads) and a regional coefficient. The sum of such margins in a farm is its economic size, expressed in European Size Units (ESU, 1 ESU is a 1200-euro SGM).
An Annual work unit (AWU) is equivalent to a worker employed on a full time basis for one year. In Spain it is 1824 hours (228 working days of 8 working hours per day).
A Livestock Unit (LSU) is equivalent to a dairy cow. The number of animals (number of heads) is converted into LSU using a set of coefficients reflecting the feed requirements of the different animal categories.
Context
European Commission Rural development policy aims to improve competitiveness in agriculture and forestry, improve the environment and countryside, improve the quality of life in rural areas and encourage the diversification of rural economies.
As agriculture has modernized and the importance of industry and services within the economy has increased, so agriculture has become much less important as a source of jobs. Consequently, increasing emphasis is placed on the role farmers can play in rural development, including forestry, biodiversity, the diversification of the rural economy to create alternative jobs and environmental protection in rural areas.
The FSS continues to adapt to provide timely and relevant data to help analyse and follow these developments.
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Farm Structure Survey in Spain - 2007 - Statistics in focus 90/2009
- National Methodological Report – FSS 2007 Spain (available on request)
Main tables
- Agriculture, see:
- Structure of agricultural holdings (t_ef)
Database
- Agriculture, see:
- Structure of agricultural holdings (ef)
Dedicated section
- Agriculture, see:
- Ad-hoc tables: Farm Structure Survey