Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - Slovakia
- Data from July 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat publication Smarter, greener, more inclusive - Indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy. It provides recent statistics on the Europe 2020 strategy of the European Union (EU), focusing on the situation in Slovakia.

Main statistical findings
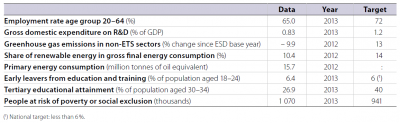
In 2010 GHG emissions in Slovakia were the same as in 2005 and thus well below the country’s long-term commitment to limit the increase in emissions to no more than 13 % by 2020. Although in 2012 Slovakia already exceeded its early school leaving target by 0.7 percentage points, the tertiary educational attainment rate deviated substantially (by 16.3 percentage points) from its long-term target. The employment rate followed the EU trend and decreased considerably after the crisis, with the employment indicator farther (6.9 percentage points gap) from its target than the EU average. In contrast, the country was closer to its renewable energies, R&D expenditure and poverty and social inclusion targets than the EU average.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Measures implemented to meet the national targets
- Early school leaving: Reforming the funding system for schools in order to remove deficiencies, increasing the integration of disadvantaged communities in the educational system, strengthening the role, status and financial remuneration of teachers at all educational levels, improving the school quality assessment system and increasing the linkage between vocational education and practice.
- Tertiary education: Reforming the funding system for higher education by introducing instruments, which discourage the retainment of non-¬performing students; reforming the accreditation procedure for higher education institutions.
- R&D: Increasing the contribution of the private sector to science, research and innovation; strengthen Slovakia’s participation in international research projects; create appropriate institutional arrangements and legal conditions enabling the transfer from knowledge to practice and improving the link between research institutions and business; preparation of the Smart Specialisation Strategy in Research, Development and Innovation in the Slovak Republic by 2020.
- Employment: Reforming active labour market policies, wider provision of public employment services; programmes promoting youth employment, including a youth guarantee scheme; tackling long-term unemployment by increasing the match between the general education system and life-long learning with the labour market needs and reducing the tax burden faced by low-income employees.
- Poverty: Effective targeting of social benefits and better harmonisation with active labour market policies; continued implementation of the childcare allowance programme; supporting economic and social integration and protecting marginalised communities; improving living conditions of people with disabilities; increasing availability and quality of social services; improving access to housing of risk-groups.
- Climate change and energy: Support the stable and due functioning of the EU ETS scheme; various measures under the Low-carbon Development Strategy of the Slovak Republic including modernisation of the public lighting system and transport infrastructure, higher energy efficiency of buildings, improved recycling and energy recovery of waste; increasing cost-effectiveness of the financial support for renewable energy sources; reform in the provision of subsidies for coal production; establishment of a credit fund for improving energy efficiency of residential buildings. For further details see Europe 2020 in Slovakia
The European Commission's 2013 country-specific recommendations
- Employment: Step up measures for reducing high youth unemployment, improving public employment services, promoting activation policies for the long-term unemployed, increasing childcare facilities and reducing the tax burden of low-paid workers.
- Education: Further promote work-based learning in companies, increase attractiveness of the teaching profession; develop more job-oriented bachelor programmes; improve access of marginalised communities to education.
- Energy: Step up efforts to improve energy efficiency, in particular in the construction and industry sectors.
- Others: Further efforts are needed for reforming the administrative system and improving the efficiency of the juridical system; take measures to fight tax evasion; improve VAT collection; continue improving the sustainability of pensions and step up a reform in the healthcare sector.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file)
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council COM(2011) 211 final.
Other information
- Regulation 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics