Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - Spain
- Data from July 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat publication Smarter, greener, more inclusive - Indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy. It provides recent statistics on the Europe 2020 strategy of the European Union (EU), focusing on the situation in Spain.
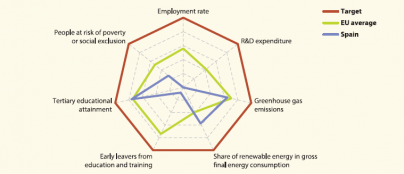
Main statistical findings
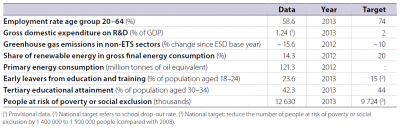
Although at some distance from its renewable energies target, Spain was still ahead of the EU average in progressing towards its 2020 commitment in 2011. The country was also slightly closer than the EU as a whole to its tertiary education target in 2012. Although GHG emissions were reduced by 4 percentage points, a 6 percentage point gap remains to the target. The indicators on employment and social inclusion deteriorated after the economic downturn, leading to a larger deviation from their targets. Despite a reduction in the early school leaving rate in the past four years, further progress is still needed. Bigger efforts than in other Member States are also needed to bring R&D expenditure in line with the national target.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Measures implemented to meet the national targets
- Employment: Establishment of new employment objectives under the Annual Employment Policy Plan 2012; development of a new system for training employed and unemployed workers; fostering employment of young workers through the launch of a dual vocational training scheme, the promotion of self-employment among the young and the provision of hiring incentives for young people with limited work experience.
- R&D expenditure: More efficient and stable provision of resources for R&D activities as set out under the Spanish Science and Technology and Innovation Strategy 2013–2020; promoting business investment in R&D; achieving better coordination between the central government and autonomous regions.
- Climate change: Development of a new environmental tax system, adoption of National Framework Waste Plan, legislative initiative regarding the calculation of carbon footprint.
- Energy efficiency: Measures aimed at improving energy efficiency in buildings through energy efficiency certification, direct support for the acquisition of energy-efficient vehicles.
- Education: Introducing education reforms including early detection of learning problems, launch of improvement programmes, increased academic time for developing core competences for academic progress, creation of a new Basic Vocational Education diploma for people who have not completed compulsory secondary education, adoption of two specific action plans to tackle early school leaving.
- Poverty and social exclusion: Active inclusion programme promoting the employment of the Roma minority, former drug dependents; ensuring effective provision of social services, in particular for children and families; mechanisms for restructuring mortgage debts of heavily indebted households.
The European Commission's 2013 country-specific recommendations
- Employment: Current policy reforms need to be further strengthened; modernise public employment services and increase the effectiveness of re-skilling training programmes for older and low-skilled workers.
- Education: Ensuring that the education and training outcomes match the labour market needs, reducing early school leaving and enhancing life-long learning to fight the high youth unemployment rate.
- Social inclusion: Effectively targeting the most marginalised though active employment policies and improving in the efficiency and effectiveness of social support.
- Energy: Structural reform in the electricity sector is needed for the electricity tariff deficit to be tackled; measures should also be taken to reform the transport sector.
- Other recommendations: Fiscal consolidation efforts to stabilise the public budgetary position; improve the efficiency of the tax system, in particular by advancing environmental taxation, reviewing corporate taxation and tackling tax fraud and evasion; enhance the business environment by removing barriers to doing business and other bottlenecks; ensure better coordination between various public administrations.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file)
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission COM(2011) 211 final
Other information
- Regulation 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics