Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - Netherlands
- Data from July 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat publication Smarter, greener, more inclusive - Indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy. It provides recent statistics on the Europe 2020 strategy of the European Union (EU), focusing on the situation in Netherlands.

Main statistical findings
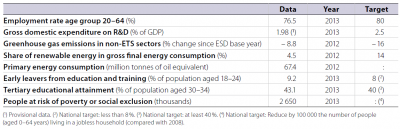
In 2012 the Netherlands already exceeded its tertiary educational attainment target. Despite the adverse impact of the economic crisis on employment and poverty rates, the country was closer to the employment and social inclusion targets than the EU average. Although remaining at some distance from the respective targets, the indicators on early school leaving and R&D expenditure have experienced favourable developments over the past few years. Efforts are needed to further reduce GHG emissions. In the area of renewable energies, in 2011 the Netherlands was among the countries farthest from their national targets.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Measures implemented to meet the national targets
- Employment: Introducing a number of reforms aimed at increasing the mobility and broadening the participation in the labour market including simplification on the law of dismissals and strengthening activation measures.
- Research and innovation: Promoting closer cooperation between academic institutes, public authorities and the private sector; encouraging private R&D spending through an Innovation Fund and tax facilities.
- Energy and climate change: Continued implementation of the Local Climate Agenda and the Green Deals Programme for collaboration with social partners on GHG reduction; launch of programmes promoting environmentally friendly behaviour such as Mobility Management, Multiyear Agreements, New Driving Style and Sustainable Logistics; introduction of an energy tax on gas and electricity, duties on motor fuels; promoting investment of enterprises in energy efficient equipment through the Energy Investment Allowance scheme; measures for increasing energy efficiency of buildings.
- Tertiary education: Measures for improving the performance of higher education and the quality of teaching and increasing the completion rate of students; staff action plans for introducing a loan system for new students.
- Early school leaving: Comprehensive policy measures for preventing absenteeism at school; support measures for the regional approach to managing early school leaving including allocation of subsidies.
- Poverty: Policy measures for promoting the access to the labour market, ensuring adequate minimum income and access to quality assistance for vulnerable groups.
The European Commission's 2013 country-specific recommendations
- Employment: Further efforts for increasing the labour market participation of second wage earners, people with migrant backgrounds, disabled and older people; take steps in reforming the tax system, the employment protection legislation and the unemployment benefit scheme in order to address disincentives to work.
- Poverty: Take measures for aligning rents with household income in the rental markets; strengthen targeted social housing policies.
- Others: Further efforts are needed for enhancing pension sustainability in view of the demographic change; measures for increasing the cost-efficiency of long-term care services; introduce reforms in the property market preventing household indebtedness; continue fiscal consolidation efforts.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file)
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council COM(2011) 211 final
Other information
- Regulation 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics