Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - Sweden
- Data from July 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat publication Smarter, greener, more inclusive - Indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy. It provides recent statistics on the Europe 2020 strategy of the European Union (EU), focusing on the situation in Sweden.
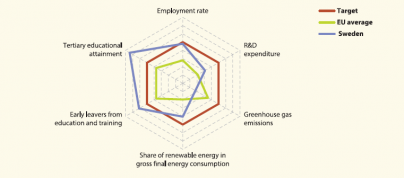
Main statistical findings
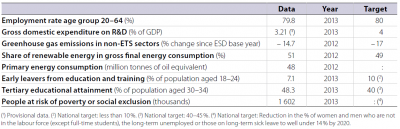
With 47.9 % of its 30 to 34 year old population having attained tertiary education in 2012, Sweden has already exceeded its national 2020 target by 7.9 percentage points. The country has also already surpassed its early school leaving target by 2.5 percentage points. Despite the slight deterioration in the labour market as a result of the crisis, Sweden had the highest employment rate in the EU in 2012 and was closer to its target than most other EU countries. Further progress is needed in order to bring the indicators on R&D expenditure, renewable energies and GHG emissions into line with the country’s 2020 targets. The gap was particularly large for GHG emissions (11 percentage points in 2010), with Sweden being further from its target than most other Member States.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Measures implemented to meet the national targets
- Employment: Preventing discrimination in the labour market, in particular for Roma people, investigating possibilities for longer working life and reinforcing the development of regional skill platforms.
- Education: Developing initiatives for reducing upper-secondary drop-out rates; incentives for improving the quality of work introduction measures; increasing the number of places in tertiary and vocational education and measures for strengthening the quality of educational programmes.
- Poverty: Measures aimed at the effective labour market introduction of young people; social assistance reforms to encourage greater labour market participation of benefit recipients; plans for reforming the design of parental benefit; increase in housing allowance for households with children and pensioners.
- R&D: Measures aimed at increasing the efficiency of the national research system, facilitating participation in transnational research cooperation, attracting prominent international researchers, promoting gender equality in research and enhancing the dissemination of research-based projects.
- Climate and energy: Initiatives aimed at increasing the energy efficiency of buildings, developing a regional plan for action for climate adaptation, strengthening R&D in the area of renewable energy.
The European Commission's 2013 country-specific recommendations
- Employment: Take further steps to increase labour market integration of low-skilled youth and people with migrant background; implement measures facilitating the transition from school to work by expanding opportunities for apprenticeships.
- Others: Remove incentives to borrow in order to sustain the high indebtedness levels of households; implement reforms in the rent-setting system; remove bottlenecks, increase efficiency and reduce costs in the construction sector in order to increase flexibility of housing supply.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file)
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission COM(2011) 211 final
Other information
- Regulation 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics