Archive:Trade in business services
- Data extracted in May-June 2017. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
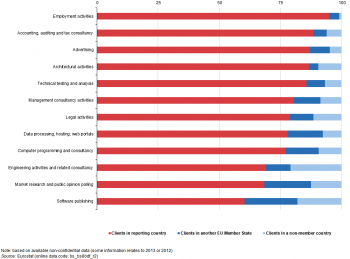
(% of turnover)
Source: Eurostat (bs_bs8bdf_r2)
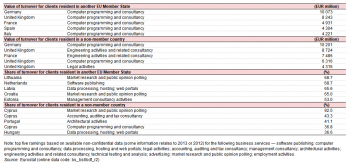
Source: Eurostat (bs_bs8bdf_r2)
Globalisation patterns in EU trade and investment is an online Eurostat publication presenting a summary of recent European Union (EU) statistics on economic aspects of globalisation, focusing on patterns of EU trade and investment.
The business services sector can be viewed as providing key inputs in the production of other goods and services. As such, it makes an important contribution to the fortunes of the whole EU-28 economy, promoting competitiveness and growth. The business services sector has expanded in recent years: this growth has been underpinned by the development of new services and more specialised tasks (including the management of supply chains and international production networks), but also reflects increased levels of outsourcing to external suppliers. These changes have provided a stimulus for the business services sector to become increasingly global in nature. Furthermore, technological changes have allowed smaller businesses to enter niche markets where previously they may have lacked the scale to trade internationally.
This subchapter provides an analysis of the turnover (sales) of EU-28 enterprises in the business services sector, according to the residence of their clients — information is presented for clients residing in the reporting country, for clients residing in another EU Member State, and for clients residing in a non-member country, in other words, outside the EU.
In 2014, almost two fifths of EU-28 sales by the software publishing sector were generated from clients residing in other countries
Figure 1 shows the proportion of business services turnover in 2014 that was accounted for by these three different sets of clients. For each of the business services shown, a majority of the EU-28’s turnover was realised by sales to clients from the reporting country (in other words, from clients residing in the domestic economy). This pattern was particularly evident for employment services and some specific professional services, whereas clients resident in other countries accounted for a higher share of total sales for activities such as computer services. Such disparities may be linked to the tradability of various services, the different modes for trading services, or barriers to entry which prevent/restrict trade in some business services.
In 2014, 95.0 % of the sales made by EU-28 employment activities were to clients from the reporting country; by contrast, the proportion of total turnover accounted for by domestic clients fell to 60.4 % for software publishing activities. Among those activities recording relatively high shares of EU-28 sales being derived from clients residing abroad, the share of turnover that was attributed to clients from other EU Member States was generally higher than that from clients residing in non-member countries. For example, close to one fifth of the total turnover generated in software publishing (21.6 %) and in market research and public opinion polling (19.2 %) was accounted for by clients residing in other EU Member States. The highest shares of turnover being realised among clients residing outside the EU-28 were recorded for engineering activities and related consultancy (20.8 %) and software publishing (18.1 %).
In 2014, the EU-28 computer programming and consultancy services sector recorded highest levels of sales generated from clients residing in other EU Member States
Looking in more detail at developments across the individual EU Member States, Table 1 shows a ranking of the turnover generated by selected business services, according to the residence of clients. In 2014, German computer programming and consultancy enterprises recorded the highest value of business services sales to clients residing in another EU Member State (EUR 10.1 billion). The same activity — computer programming and consultancy — also accounted for the second to fifth highest value of sales, as made by British, French, Spanish and Italian enterprises.
Concerning sales to clients residing outside the EU, the highest level of turnover was generated once again by German computer programming and consultancy services (EUR 10.2 billion), while British computer programming and consultancy enterprises had the fourth highest level of sales to non-member countries. Aside from these, the top five ranking featured a wider range of activities, with a high value of sales to clients residing outside the EU among British enterprises engaged in engineering activities and related consultancy and legal activities and French enterprises engaged in engineering activities and related consultancy.
While the rankings of overall turnover are unsurprisingly dominated by some of the largest EU Member States, the second half of the table presents relative measures based on the proportion of national turnover that was generated by clients from abroad. In 2014, more than two thirds (68.7 %) of all sales made in Lithuania by market research and public opinion polling enterprises was derived from clients residing in other EU Member States; an identical share was recorded for Dutch software publishing enterprises.
The share of total turnover that was generated from clients residing in non-member countries peaked at 92.5 % for Cypriot market research and public opinion polling enterprises; the only time a majority of sales were generated from clients residing outside the EU-28. The next highest shares were recorded for accounting, auditing and tax consultancy services in Cyprus (43.3 % of their turnover was generated from clients resident in a non-member country) and architectural activities in Portugal (where clients resident in a non-member country accounted for 41.1 % of sales).
See also
- Name of related Statistics Explained article
- Name of related online publication in Statistics Explained (online publication)
- Name of related Statistics in focus article in Statistics Explained
- Subtitle of Statistics in focus article=PDF main title - Statistics in focus x/YYYY
Further Eurostat information
Data visualisation
- Regional Statistics Illustrated - select statistical domain 'xxx' (= Agriculture, Economy, Education, Health, Information society, Labour market, Population, Science and technology, Tourism or Transport) (top right)
Publications
Publications in Statistics Explained (either online publications or Statistics in focus) should be in 'See also' above
Main tables
- Title(s) of second level folder (if any)
- Title(s) of third level folder (if any)
Database
- Title(s) of second level folder (if any)
- Title(s) of third level folder (if any)
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
<link to ESMS file, methodological publications, survey manuals, etc.>
- Crime and criminal justice (ESMS metadata file — crim_esms)
- Title of the publication
Source data for tables, figures and maps (MS Excel)
Other information
<Regulations and other legal texts, communications from the Commission, administrative notes, Policy documents, …>
- Regulation (EC) No 1737/2005 (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32005R1737:EN:NOT Regulation (EC) No 1737/2005]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
- Directive 2003/86/EC (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32003L0086:EN:NOT Directive 2003/86/EC]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
- Commission Decision 2003/86/EC (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32003D0086:EN:NOT Commission Decision 2003/86/EC]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
<For other documents such as Commission Proposals or Reports, see EUR-Lex search by natural number>
<For linking to database table, otherwise remove: {{{title}}} ({{{code}}})>
External links
Notes
[[Category:<Subtheme category name(s)>|Name of the statistical article]] [[Category:<Statistical article>|Name of the statistical article]]