Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - Romania
- Data from July 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat publication Smarter, greener, more inclusive - Indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy. It provides recent statistics on the Europe 2020 strategy of the European Union (EU), focusing on the situation in Romania.
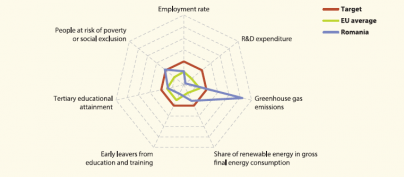
Main statistical findings
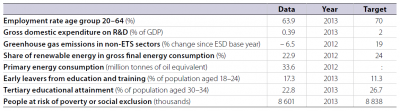
By 2010 Romania had reduced its GHG emissions by 8 % (compared with 2005), thus remaining well below its target. Romania was also one of the two Member States that already managed to reach their national poverty reduction targets in 2011. However, the country’s indicators on employment, early school leaving and R&D expenditure deteriorated compared to 2008 levels, increasing the distance to the respective national targets. Although still farther from its target than the EU average, Romania achieved sizeable progress in raising the tertiary educational attainment rate by 5.8 percentage points between 2008 and 2012. The share of renewable energies moved closer to the country’s commitments, with a gap of 2.6 percentage points to be closed by 2020.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Measures implemented to meet the national targets
- Employment: Fighting illegal work, increasing the flexibility of employment procedures, mitigating in-work poverty by increasing the minimum gross wage, facilitating the transition of the unemployed to the labour market; increasing the employability of young people and persons living in rural areas.
- R&D: Increasing the performance of RDI systems, by developing the technology and human resource base for research and enhancing the evaluation, classification and certification of public R&D institutes; establishment of the National Strategy for RDI 2014–2020; supporting private investment initiatives in R&D.
- Climate change: Continued implementation of renewable energy projects and actions aimed at modernising the road transport sector; launch of a project for carbon capture and storage (CCS) and a campaign for reforestation.
- Renewable energy: Progress in enhancing the delivery of the green certificates scheme; provision of financial support for renewable energies investments; measures for improving the capacity of the electricity and heat production from renewables.
- Energy efficiency: implementation of a state aid support scheme for high efficiency cogeneration; financial support for the rehabilitation of centralised district heating systems and residential buildings.
- Education: Implementation of social support programmes aimed at combating early school leaving; introducing reforms in preparatory class arrangements; action plans for increasing the inclusiveness and quality of education; re-launch of the National Strategy on Reducing Early School Leaving; measures aimed at increasing the relevance of higher education to the labour market needs; launching social scholarships and programmes for disadvantaged students.
- Poverty: Increasing the quality of social assistance services and improving the access of the most disadvantaged groups to basic social services; special support actions targeted at children with disabilities and children from disadvantaged groups.
The European Commission's 2013 country-specific recommendations
- Employment: Strengthen active labour market policies; ensure in-time implementation of the National Plan for Youth Employment; promote employability of older workers.
- Poverty: Further measures for improving the effectiveness and efficiency of social benefits, in particular for children; ensure progress with the implementation of the National Roma Integration Strategy.
- Education: Continue ongoing efforts in reforming the education system; ensure tertiary education matched the needs of the labour market.
- Others: Improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the health-care system; take measures for enforcing tax compliance and improving the capacity of public administration; implement reforms in the markets for energy and transport; extend broadband coverage.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file)
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council COM(2011) 211 final
Other information
- Regulation 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics