Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - Latvia
- Data from July 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat publication Smarter, greener, more inclusive - Indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy. It provides recent statistics on the Europe 2020 strategy of the European Union (EU), focusing on the situation in Latvia.

Main statistical findings
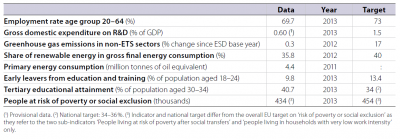
In 2012 Latvia showed significant progress towards both of its education targets. By increasing the tertiary education rate by 10 percentage points and reducing the number of early school leavers by 5 percentage points in the period 2008 to 2012, Latvia managed to exceed these two Europe 2020 benchmarks in advance. Despite the 7 % rise in GHG emissions between 2005 and 2010, the country is still within the limits of its 2020 target of increasing emissions by no more than 17 %. In 2012 the employment rate stabilised after a period of deterioration in the years 2008 to 2011, and the distance to the national target was shorter than the EU average. Although in 2012 the trend of increasing poverty and social exclusion was halted, Latvia still remained at a greater distance from its target than the EU average. Further progress in the uptake of renewable energies and increasing R&D expenditure are needed for the gaps to these targets to be closed.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Measures implemented to meet the national targets
- Employment: Measures and support mechanism related to improvement in the training programmes for the unemployed, reduction in youth unemployment, efficient transition of the long-term unemployed to the labour market; promotion of self-employment and entrepreneurship.
- Early school leaving: Policies aimed at increasing the access to primary and secondary education; introduction of modern teaching methods; enhancement and structural reform of vocational education.
- R&D: Improving the quality, efficiency and international competitiveness of R&D; promoting cooperation between scientists and entrepreneurs; supporting the development of innovative enterprises.
- Tertiary education: Modernising tertiary education, improving the material-technical base of higher education institutions, increasing the access to and the quality of higher studies and promoting internationalisation.
- Poverty: Reducing the tax burden of the population at risk of poverty, active labour market policy measures targeted at the most disadvantaged groups; measures for limiting discrimination and strengthening civil society participation.
- Energy efficiency: Measures aimed at improving insulation of buildings; financial support for projects aimed at increasing energy efficiency of buildings; improving energy efficiency in heat energy production.
- Renewable energy: Adjustments in the legal basis for supporting the uptake of renewables in energy consumption and production; allocation of financial resources to the production of renewable energy; promoting the use of biofuels in the transport sector.
- GHG emissions: Measures for reducing the non-Emissions Trading System (ETS) sector emissions; supporting related research and innovation projects and information and awareness raising campaigns.
The European Commission's 2013 country-specific recommendations
- Employment: Pursue further measures for tackling youth unemployment such as introducing Youth Guarantee and strengthening vocational education and training.
- Poverty: Improve the coverage and adequacy of social assistance and introduce special measures for reducing child poverty.
- Energy efficiency: Speed up the implementation of housing insulation projects.
- Education and research: Continue the planned reforms in higher education and take further measures for modernising research institutions.
- Others: Shift taxes towards property or the environment; take further measures for increasing the efficiency and quality of the judiciary.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file)
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council COM(2011) 211 final
Other information
- Regulation 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics