1.1. Contact organisation
ZEW - Leibniz-Zentrum für Europäische Wirtschaftsforschung GmbH Mannheim
(Centre for European Economic Research)
1.2. Contact organisation unit
Department Economics of Innovation and Industrial Dynamics
1.3. Contact name
Confidential because of GDPR
1.4. Contact person function
Confidential because of GDPR
1.5. Contact mail address
ZEW
L 7, 1
68161 Mannheim
Germany
1.6. Contact email address
Confidential because of GDPR
1.7. Contact phone number
Confidential because of GDPR
1.8. Contact fax number
Confidential because of GDPR
2.1. Metadata last certified
28 May 2024
2.2. Metadata last posted
31 October 2022
2.3. Metadata last update
28 May 2024
3.1. Data description
The Community Innovation Survey (CIS) is a survey about innovation activities in enterprises. The survey is designed to collect the information on types of innovation, processes of development of innovation like cooperation patterns, financing and expenditure, objectives of innovation activities or barriers for initiating or implementing innovation.
The CIS provides statistics by type of innovators, economic activity and size class of enterprises. The survey is currently carried out every two years across the EU Member States, EFTA countries and EU candidate countries.
In order to ensure comparability across countries, Eurostat together with the countries develops a Harmonised Data Collection (HDC) questionnaire and drafts the methodological recommendations for implementation of each survey round.
CIS 2020 is a second in a row to implement concepts and methodology of the Oslo Manual 4th Edition revised in 2018. The changes in the CIS driven by the revision of the manual and their impact on collected indicators are described in the Statistics Explained article: Community Innovation Survey – new features.
The legal framework for CIS since 2012 is the Commission Regulation No 995/2012 that establishes the quality conditions for the data collection and transmission and identifies the obligatory cross-coverage of economic sectors, size class of enterprises and innovation indicators. The target population are enterprises with at least 10 employees classified in the core NACE economic sectors (see 3.3). Further activities may be covered on a voluntary basis in national datasets. Most statistics are based on the 3-year reference period (t, t-1, t-2), but some use only one calendar year (t or t-2). Please refer to the Annex section of the European metadata (ESMS) for details of the time coverage of collected indicators.
3.2. Classification system
Indicators related to the enterprises are classified by country, economic activity (NACE Rev. 2), size class of enterprises and type of innovation.
The main typology of classification of enterprises in reference to innovation is the distinction between innovation-active enterprises (INN) and not innovation-active enterprises (NINN).
The enterprise is considered as innovative (INN) if during the reference period it successfully introduced a a) product or a) business process innovation, c) completed but not yet implemented the innovation, d) had ongoing innovation activities, e) abandoned innovation activities or was f) engaged in in-house R&D or R&D contracted out. Non-innovative (NINN) enterprises had no innovation activity mentioned above whatsoever during the reference period.
3.3. Coverage - sector
CIS covers main economic sectors according to NACE Rev.2 broken down by size class of enterprises and type of innovation activity.
3.3.1. Main economic sectors covered - NACE Rev.2
In accordance with Commission Regulation 995/2012 on innovation statistics, the following industries and services are included in the core target population. Results are made available with these following breakdowns :
All NACE – Core NACE (NACE Rev. 2 sections & divisions B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73 )
CORE INDUSTRY (excluding construction) (NACE Rev. 2 SECTIONS B_C_D_E)
10-12: Manufacture of food products, beverages and tobacco
13-15: Manufacture of textiles, wearing apparel, leather and related products
16-18: Manufacture of wood, paper, printing and reproduction
20: Manufacture of chemicals and chemical products
21: Manufacture of basic pharmaceutical products and pharmaceutical preparations
19-22: Manufacture of petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, rubber and plastic products
23: Manufacture of other non-metallic mineral products
24: Manufacture of basic metals
25: Manufacture of fabricated metal products, except machinery and equipment
26: Manufacture of computer, electronic and optical products
25-30: Manufacture of fabricated metal products (except machinery and equipment), computer, electronic and optical products, electrical equipment, motor vehicles and other transport equipment
31-33: Manufacture of furniture; jewellery, musical instruments, toys; repair and installation of machinery and equipment
D: ELECTRICITY, GAS, STEAM AND AIR CONDITIONING SUPPLY
E: WATER SUPPLY; SEWERAGE, WASTE MANAGEMENT AND REMEDIATION ACTIVITIES
36: Water collection, treatment and supply
37-39: Sewerage, waste management, remediation activities
CORE SERVICES (NACE Rev. 2 sections & divisions 46-H-J-K-71-72-73)(NACE code in the tables = G46-M73_INN)
46: Wholesale trade, except of motor vehicles and motorcycles
H: TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
49-51: Land transport and transport via pipelines, water transport and air transport
52-53: Warehousing and support activities for transportation and postal and courier activities
J: INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION
58: Publishing activities
61: Telecommunications
62: Computer programming, consultancy and related activities
63: Information service activities
K: FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE ACTIVITIES
64: Financial service activities, except insurance and pension funding
65: Insurance, reinsurance and pension funding, except compulsory social security
66: Activities auxiliary to financial services and insurance activities
M: PROFESSIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL ACTIVITIES
71: Architectural and engineering activities; technical testing and analysis
72: Scientific research and development
73: Advertising and market research
71-73: Architectural and engineering activities; technical testing and analysis; Scientific research and development; Advertising and market research
3.3.1.1. Main economic sectors covered - NACE Rev.2 - national particularities
The German CIS 2018 also covers the following NACE groups and divisions:
69, 70.2, 74, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82
3.3.2. Sector coverage - size class
In accordance with Commission Regulation 995/2012 on innovation statistics, the following size classes of enterprises according to number of employees are included in the core target population of the CIS:
- 10 - 49 employees
- 50 - 249 employees
- 250 or more employees
3.3.2.1. Sector coverage - size class - national particularities
The German CIS 2018 is using 'person employed' as classification unit for size class of enterprises.
The survey also covers enterprises with 5 to 9 employed persons.
The sample of the German CIS 2018 has been stratified by 8 size classes: 5-9, 10-19, 20-49, 50-99, 100-249, 250-499, 500-999, 1000+
3.4. Statistical concepts and definitions
The description of concepts, definitions and main statistical variables is available in CIS 2020 European metadata file (ESMS) Results of the community innovation survey 2020 (CIS2020) (inn_cis12) in Eurostat database.
3.5. Statistical unit
The statistical unit of the German CIS 2018 is the legal unit according to the definition of legal unit in the Business Register of the Statistical Office of the Federal Republic of Germany.
There are some deviations to this rule in case of large, complex enterprises that are active in different NACE divisions. For some of these large, complex enterprises, the statistical unit is the business unit that best matches the activities of the enterprise that fall under a single NACE division.
3.6. Statistical population
Core target population are all enterprises in CORE NACE activities (see 3.3.1) with 10 or more persons employed.
3.7. Reference area
The German CIS 2018 covers all enterprises in the statistical population that are located within the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany.
There is not breakdown of CIS 2018 results by NUTS regions available. The only breakdown available is by Western Germany vs. Eastern Germany.
The microdata nevertheless contain information on the location of an enterprise by NUTS 3-digit level.
3.8. Coverage - Time
Several rounds of Community Innovation Survey have been conducted so far at two-year interval since end of 90’s.
3.8.1. Participation in the CIS waves
| CIS wave | Reference period | Participation | Comment (deviation from reference period) |
| CIS2 | 1994-1996 | yes | no |
| CIS3 | 1998-2000 | yes | no |
| CIS light | 2002-2003* | yes | no |
| CIS4 | 2002-2004 | yes | no |
| CIS2006 | 2004-2006 | yes | no |
| CIS2008 | 2006-2008 | yes | no |
| CIS2010 | 2008-2010 | yes | no |
| CIS2012 | 2010-2012 | yes | no |
| CIS2014 | 2012-2014 | yes | no |
| CIS2016 | 2014-2016 | yes | no |
| CIS2018 | 2016-2018 | yes | no |
| CIS2020 | 2018-2020 | yes | no |
*two reference periods can be distinguished for CIS light: 2000-2002 and 2001-2003
3.9. Base period
Not relevant.
CIS indicators are available according to 3 units of measure:
NR: Number for number of enterprises and number of persons employed.
THS_EUR: Thousands of euros. All financial variables are provided in thousands of euros, i.e. Turnover or Innovation expenditure.
PC: Percentage. The percentage is the ratio between the selected combinations of indicators.
For CIS 2020, the time covered by the survey is the 3-year period from the beginning of 2018 to the end of 2020.
Some questions and indicators refer to one year — 2020.
The list of indicators covering the 3-year period and referring to one year according to the HDC is available in the Annex section of the European metadata (ESMS).
6.1. Institutional Mandate - legal acts and other agreements
CIS surveys are based on the Commission Regulation No 995/2012, implementing Decision No 1608/2003/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the production and development of Community statistics on science and technology.
This Regulation establishes innovation statistics on a statutory basis and makes the delivery of certain variables compulsory e.g. innovation activities, cooperation, development, expenditures and turnover (see the Regulation). Each survey wave may additionally include further variables.
In addition, the Regulation defines the obligatory cross-coverage of economic sectors and size class of enterprises.
6.1.1. National legislation
European legislation applies.
6.2. Institutional Mandate - data sharing
Not requested.
CIS data are transmitted to Eurostat via EDAMIS using the secured transmission system.
7.1. Confidentiality - policy
No confidentiality policy.
7.2. Confidentiality - data treatment
Does not apply.
8.1. Release calendar
National results of the CIS 2020 were released on February 1st, 2022 (Indicator Study, see attached pdf "Indikatorenbericht").
At the same time, 47 short innovation reports on individual industries were released (see https://www.zew.de/en/publications/zew-expertises-research-reports/research-reports/innovations/zew-sector-reports-on-innovation, only German version available).
A technical documentation of the CIS 2020 will be publised in November 2022 (see https://www.zew.de/publikationen/dokumentation-zur-innovationserhebung-2021, only German version available).
Annexes:
Report on national results of the German CIS 2020
8.2. Release calendar access
There is no ex-ante release calendar for the German CIS.
8.3. Release policy - user access
All reports on the German CIS 2020 results are available for free to everyone.
Result tables (Excel format) are available on the website of ZEW (German and English versions):
https://www.zew.de/en/publications/zew-expertises-research-reports/research-reports/innovations/mannheim-innovation-panel-the-annual-german-innovation-survey/documentations-table-appendix
Differently to the CIS in most other EU member states, the German CIS is conducted every year. Results are therefore published every year. Results of an innovation survey with the reference year t are usually released at the end of January of year t+2.
Accessibility and clarity refer to the simplicity and ease for users to access statistics using simple and user-friendly procedure, obtaining them in an expected form and within an acceptable time period, with the appropriate user information and assistance: a global context which finally enables them to make optimum use of the statistics.
10.1. Dissemination format - News release
See below.
10.1.1. Availability of the releases
| Dissemination and access | Availability | Comments, links, ... |
| Press release | yes, along with the publication of the national report | https://www.zew.de/en/press/latest-press-releases/covid-19-pandemic-is-both-an-obstacle-and-an-impetus-for-innovation |
| Access to public free of charge | through ZEW website: www.zew.de/innovation | |
| Access to public restricted (membership/password/part of data provided, etc) | none |
10.2. Dissemination format - Publications
- Online database (containing all/most results) : https://www.zew.de/en/publications/zew-expertises-research-reports/research-reports/innovations/mannheim-innovation-panel-the-annual-german-innovation-survey/core-indicators
https://www.zew.de/en/publications/zew-expertises-research-reports/research-reports/innovations/mannheim-innovation-panel-the-annual-german-innovation-survey/focus-indicators
https://www.zew.de/en/publications/zew-expertises-research-reports/research-reports/innovations/mannheim-innovation-panel-the-annual-german-innovation-survey/documentations-table-appendix
- Analytical publication (referring to all/most results) : https://www.zew.de/en/publications/dokumentation-zur-innovationserhebung-2021-1
- Analytical publication (referring to specific results, e.g. only for one sector or one specific aspect) : https://www.zew.de/en/publications/zew-expertises-research-reports/research-reports/innovations/mannheim-innovation-panel-the-annual-german-innovation-survey/innovation-survey-academic-papers
10.3. Dissemination format - online database
https://www.zew.de/en/publications/zew-expertises-research-reports/research-reports/innovations/mannheim-innovation-panel-the-annual-german-innovation-survey
10.3.1. Data tables - consultations
Not requested.
10.4. Dissemination format - microdata access
see 10.4.1.
10.4.1. Dissemination of microdata
| Mean of dissemination | Availability of microdata | Comments, links, ... |
| Eurostat SAFE centre | x | |
| National SAFE centre | x | |
| Eurostat: partially anonymised data (SUF) | x | |
| National : partially anonymised data | x |
10.5. Dissemination format - other
No other means of dissemination.
10.5.1. Metadata - consultations
Not requested.
10.6. Documentation on methodology
The methodology is documented in a separate report: Rammer, Christian and Torben Schubert (2022), Dokumentation zu den Innovationserhebungen 2017 bis 2021, Mannheim.
10.6.1. Metadata completeness - rate
Not requested.
10.7. Quality management - documentation
For data collection, data processing and data analysis, the standard quality procedures for enterprise surveys are applied, including double entry of data from paper questionnaires and codes for detecting likely data errors and inconsistencies.
The quality of the German CIS 2020 is assessed to be very good. Owing to the fact that innovation surveys are conducted annually in Germany in the form of a panel survey, enterprises do fully understand the underlying concepts and questions and are prepared to provide the demanded information in high quality, including information on innovation expenditures. The panel nature of the survey furthermore offers the opportunity to cross-check the information provided by enterprises with information from previous years for the same enterprise, which eases the identification of potential errors in the data.
No quality report at the national level has been produced for CIS 2020 in Germany.
11.1. Quality assurance
For data collection, data processing and data analysis, the standard quality procedures for enterprise surveys are applied, including double entry of data from paper questionnaires and codes for detecting likely data errors and inconsistencies.
11.2. Quality management - assessment
The quality of the German CIS 2020 is assessed to be very good. Owing to the fact that innovation surveys are conducted annually in Germany in the form of a panel survey, enterprises do fully understand the underlying concepts and questions and are prepared to provide the demanded information in high quality, including information on innovation expenditures. The panel nature of the survey furthermore offers the opportunity to cross-check the information provided by enterprises with information from previous years for the same enterprise, which eases the identification of potential errors in the data.
Relevance is the degree to which statistics meet current and potential users’ needs. It includes the production of all needed statistics and the extent to which concepts used (definitions, classifications etc.) reflect user needs. The aim is to describe the extent to which the statistics are useful to, and used by, the broadest array of users. For this purpose, statisticians need to compile information, firstly about their users and their needs.
The CIS is based on a common questionnaire and a common survey methodology in order to achieve comparable, harmonised and high quality results for EU Member States, EFTA countries, Candidates and Associated countries.
12.1. Relevance - User Needs
User needs are identified through the scientific advisory board of the German CIS. The advisory board includes representatives from academia (universities, research institutes), industry (industry associations), policy (Federal Ministries, Expert Commission on Research and Innovation) as well as from statistical bodies (Federal Statistical Office, organisation that conducts the R&D survey for the enterprise sector).
12.1.1. Needs at national level
| User group | Short description of user group | Main needs for CIS data of the user group Users’ needs |
| 1. Institutions - Federal government | Policy officers in Federal Ministries who design and deliver government policies | Up-to-date information on innovation activities in the enterprise sector, broken down by size, sector, type of innovation, incl. international comparison |
| 1. Institutions - State governments | Policy officers in Ministries of Federal States who design and deliver state government policies |
Up-to-date information on innovation activities in the enterprise sector in the respective Federal State, broken down by size, sector, type of innovation, incl. comparison to other regions (both national and international) |
| 2. Social actors - Industry associations, unions, other stakeholders | Experts in industry association, unions and other stakeholders who are engaged in designing and evaluating innovation policies. | Up-to-date information on innovation activities in the relevant industry, broken down by size, type of innovation, incl. international comparison for the same industry |
| 4. Researchers and students | Researchers at universities and other public research organisations | Micro-data, preferable panel data |
12.2. Relevance - User Satisfaction
Satisfaction of users of CIS 2020 is assessed to be high based on the number of individuals and users that use tabulated results, reports and micro-data.
12.3. Completeness
There are no specific issues with completeness of the German CIS 2020.
The tabulated results of the German CIS 2020 include all mandatory variables.
12.3.1. Data completeness - rate
Not requested.
13.1. Accuracy - overall
Accuracy in the statistical sense denotes the closeness of computations or estimates to the exact or true values. Statistics are not equal with the true values because of variability (the statistics change from implementation to implementation of the survey due to random effects) and bias (the average of the possible values of the statistics from implementation to implementation is not equal to the true value due to systematic effects).
13.2. Sampling error
That part of the difference between a population value and an estimate thereof, derived from a random sample, which is due to the fact that only a subset of the population is enumerated.
13.2.1. Sampling error - indicators
The main indicator used to measure sampling errors for CIS data is the coefficient of variation (CV).
Coefficient of Variation= (Square root of the estimate of the sampling variance) / (Estimated value)
Formula:
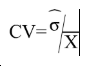
where
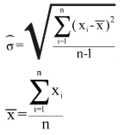
13.2.1.1. Coefficient of variations for key variables
Coefficient of variation (%) for key variables by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 and more employees
| NACE |
Size class |
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
| Core NACE (B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73) |
Total |
58,5% |
99,7% |
147,2% |
| Core industry (B_C_D_E - excluding construction) |
Total |
59,3% |
97,9% |
150,0% |
| Core Services (46-H-J-K-71-72-73) |
Total |
57,1% |
102,5% |
142,6% |
[1] = Coefficient of variation for the percentage of innovative enterprises (INN) in the total population of enterprises (ENT20)
[2] = Coefficient of variation for the turnover of product innovative enterprises with new or improved products (TUR_PRD_NEW_MKT), as a percentage of total turnover of product innovative enterprises [TUR20,INNO_PRD].
[3] = Coefficient of variation for percentage of product and/or process innovative enterprises (incl. enterprises with abandoned and or on-going activities) involved in any innovation co-operation arrangement [COOP_ALL,INN], as a percentage of innovative enterprises (INN).
13.2.1.2. Variance estimation method
see 13.2.1
13.3. Non-sampling error
Non-sampling errors occur in all phases of a survey. They add to the sampling errors (if present) and contribute to decreasing overall accuracy. It is important to assess their relative weight in the total error and devote appropriate resources for their control and assessment.
13.3.1. Coverage error
Coverage errors (or frame errors) are due to divergences between the target population and the frame population. The frame population is the set of target population members that has a chance to be selected into the survey sample. It is a listing of all items in the population from which the sample is drawn that contains contact details as well as sufficient information to perform stratification and sampling.
13.3.1.1. Over-coverage - rate
Not requested.
13.3.1.2. Common units - proportion
Not requested.
13.3.1.3. Under covered groups of the target population
No under covered groups.
13.3.1.4. Coverage errors in coefficient variation
None.
13.3.2. Measurement error
Measurement errors occur during data collection and generate bias by recording values different than the true ones. The survey questionnaire used for data collection may have led to the recording of wrong values, or there may be respondent or interviewer bias.
13.3.2.1. Measures for reducing measurement errors
The main approach to detect measurement errors are comparison of enterprise responses with responses from previous years for each variable. If no such information is available, outliers (based on the mean and standard deviation within a stratum for the respective variable) are identified and analysed.
13.3.3. Non response error
Non response occurs when a survey fails to collect data on all survey variables from all the population units designated for data collection in a sample or complete enumeration.
There are two types of non-response:
1) Unit non-response, which occurs when no data (or so little as to be unusable) are collected about a population unit designated for data collection.
a) Un-weighted unit non-response rate (%) = 100*(Number of units with no response or not usable response) / (Total number of in-scope (eligible) units in the sample)
b) Weighted unit non-response rate (%) = 100*(Number of weighted units with no response or not usable response) / (Total number of in-scope (eligible) units in the sample)
2) Item non-response, which occurs when only data on some, but not all survey data items are collected about a population unit designated for data collection.
a) Un-weighted item non-response rate (%) = 100*(Number of units with no response at all for the item) / (Total number of eligible, for the item, units in the sample i.e. filters have to be taken into account)
13.3.3.1. Unit non-response - rate
See below.
13.3.3.1.1. Un-weighted and weighted unit non-response rate by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 or more employed persons
Un-weighted and weighted unit non-response rate by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 or more persons employed
| NACE | Number of eligible units with no response | Total number of eligible units in the sample | Un-weighted unit non-response rate (%) | Weighted unit non-response rate (%) |
| Core NACE (B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73) | 9051 | 18471 | 49.0 | |
| Core industry (B_C_D_E - excluding construction) | 5634 | 12093 | 46.6 | |
| Core Services (46-H-J-K-71-72-73) | 3417 | 6378 | 53.6 |
The number of eligible units is the number of sample units, which indeed belong to the target population.
13.3.3.1.2. Maximum number of recalls/reminders before coding
Up to four reminders were made, combining written, e-mail and telephone reminders.
13.3.3.2. Item non-response - rate
See below.
13.3.3.2.1. Item non-response rate for Turnover (in Core NACE: B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73 enterprises with 10 or more employed persons)
Item non-response rate for Turnover (in Core NACE: B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73 enterprises with 10 or persons employed).
| Item non-response rate (un-weighted) | Imputation | If imputed, describe method used, mentioning which auxiliary information or stratification is used | |
| Turnover | 0.00 |
13.3.3.2.2. Item non response rate for new questions
Item non-response rate for new questions in CIS t (in Core NACE: B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73 enterprises with 10 or more employees)
| NEW QUESTIONS IN CIS 2020 | Inclusion in national questionnaire | Item non response rate (un-weighted) | Comments |
| 2.2 Market conditions faced by enterprise | yes | 8.0% | |
| 2.8 Factors related to climate change | yes | 7.8% | |
| 3.16 Innovations with environmental benefits | yes | 7.1% | combined item non response rate of question on environmental innovation within the enterprise (8.0%) and environmental innovation through the use of products (6.2%) |
| 3.17 Factors driving environmental innovations | yes | 9.9% |
13.3.4. Processing error
none
13.3.5. Model assumption error
Not requested.
Timeliness and punctuality refer to time and dates, but in a different manner.
14.1. Timeliness
The timeliness of statistics reflects the length of time between data availability and the event or phenomenon they describe.
14.1.1. Time lag - first result
Timeliness of national data – date of first release of national level : February 1st, 2022
14.1.2. Time lag - final result
Not requested.
14.2. Punctuality
Punctuality refers to the time lag between the release date of data and the target date on which they were scheduled for release as announced officially.
14.2.1. Punctuality - delivery and publication
Date of transmission of complete and validated data to Eurostat (Number of days between that data and 30 June 2022) : 14 days (delivery of final, validated data at July 14th, 2022)
Comparability aims at measuring the impact of differences in applied statistical concepts and definitions on the comparison of statistics between geographical areas, non-geographical domains, or over time.
The coherence of statistical outputs refers to the degree to which the statistical processes by which they were generated used the same concepts (classifications, definitions, and target populations) and harmonised methods. Coherent statistical outputs have the potential to be validly combined and used jointly.
15.1. Comparability - geographical
The same international standards, concepts and definitions (Oslo manual or Eurostat guidelines) have been applied for all geographical areas of Germany.
15.1.1. Asymmetry for mirror flow statistics - coefficient
Not requested.
15.1.2. National questionnaire – compliance with Eurostat model questionnaire
Methodological deviations from the CIS Harmonised Data Collection (HDC)
| Comment | |
| 2.3, 2.7, 3.9, 3.14, 3.15, 4.8, 4.9 | Questions were not included due to length restriction of national CIS |
| 3.11 | 3.11 was included in a different design in order to collect data on the use of the newly introduced R&D tax credit which came into force in 2020. |
| Changes in the filtering compared to HDC | Comment |
| none | |
15.1.3. National questionnaire – additional questions
Methodological deviations from the CIS Harmonised Data Collection (HDC)
| Additional questions in national questionnaire (not included in HDC) | Comment |
| Number of part-time employed persons; Share of exports to the UK; Share of turnover of main group of products/services; Market share of main group of products/services; World-first product innovations; Cost reduction owing to process innovation; Number of R&D personnel; Expenditure for own R&D personnel; Capital expenditure for innovation; Total innovation expenditure planned for 2021 and 2022; Use of artificial intelligence in the enterprise; Relevance and consequences of the Covid-19 pandemics (6 questions in total); Total expenditure on personnel; Total expenditure on materials, services, energy and other operating costs; Amount of fixed capital (property, plant & equipment); Profit margin | |
15.2. Comparability - over time
Due to important methodological changes driven by Oslo Manual 2018, CIS 2018 and CIS 2020 cannot be directly compared with previous CIS waves.
15.2.1. Length of comparable time series
Not requested.
15.3. Coherence - cross domain
See the comparison between SBS and CIS data in the section 15.3.3 below.
15.3.1. Coherence - sub annual and annual statistics
Not requested.
15.3.2. Coherence - National Accounts
Not requested.
15.3.3. Coherence – Structural Business Statistics (SBS)
This part compares key variables for aggregated CIS data with SBS data
Definition of relative difference between CIS and SBS data: DIFF = (SBS/CIS)*100
Comparison between SBS and CIS data (relative difference) by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 or more persons employed
| NACE | Size class | Number of enterprises (SBS/CIS)* | Number of persons employed (SBS/CIS)* | Total Turnover (SBS/CIS)* |
| Core NACE (B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73) | Total | 100.2 | 98.9 | 90.5 |
| Core industry (B_C_D_E - excluding construction) | Total | 100.2 | 99.4 | 99.4 |
| Core Services (46-H-J-K-71-72-73) | Total | 100.3 | 98.2 | 80.9 |
* Numbers are to be provided for the last year of the reference period (t)
Comment: Higher total turnover in CIS is due to financial services (NACE K) which is based on CIS definition (gross interest received, gross premium written) while SBS includes only turnover on which VAT is applied. Higher number of employed persons due to inlcusion of self-employed persons and civil servants in CIS data, which are not included in German business register data.
15.4. Coherence - internal
Not requested.
Confidential information on the production cost of the CIS.
16.1. Cost
The assessment of costs associated with a statistical product is a rather complicated task since there must exist a mechanism for appointing portions of shared costs (for instance the business register or shared IT resources and dissemination channels) and overheads (office space, utility bills etc). The assessment must become detailed and clear enough so that international comparisons among agencies of different structures are feasible.
For measuring the cost on statistical offices, Eurostat proposes to make use of the following very short calculation, even if Eurostat is aware of the fact that such a measure may be complicated.
| Costs for the statistical authority | In thousands of national currency |
| Total cost (in thousand currency units) | not available |
| Staff cost (in %) | not available |
| Other direct cost (in %) | not available |
| Overheads (in %) | not available |
National currency used for this amount:
17.1. Data revision - policy
Not requested.
17.2. Data revision - practice
Not requested.
17.2.1. Data revision - average size
Not requested.
18.1. Source data
See below
18.1.1. Sampling frame (or census frame)
The statistical business register of the German national statistical office (Destatis) is not accessible for third parties for purposes of sampling. Instead, a database of the largest German credit rating agency (CREDITREFORM) was used. This database contains information on virtually all enterprises with more than 5 employees in Germany. This
database is processed by ZEW in order to use it for sampling purposes. The data base contains about 3.3 million economically active enterprises, which corresponds to the number of economically active enterprises reported by Destatis based on the business register.
18.1.2. Sampling design
The German CIS 2020 had a total number of 896 strata (56 NACE divisions, 8 size classes, 2 regions). Random sampling with known and disproportional selection probabilities based on the variance of innovation activities per stratum observed in prior and the number of enterprises in a stratum’s total population was applied.
18.1.3. Target population and sample size
| Sample/census indicator | Number of enterprises |
| Target population | 160882 |
| Sample | 21188 |
| In case of combination sample/census: | |
| Sampled units | 17818 |
| Enumerated units/census | 3370 |
| Overall sample rate (overall sample/target population) | 15.9 |
18.1.4. Data source for pre-filled variables
Variables and indicators filled or prefilled from other sources.
| Variables/Indicators | Source | Reference year |
| Age | Mannheim Enterprise Sample | 2020 |
| Turnover, no. of employed persons | Mannheim Enterprise Sample (only in case a firm refused to report the variables) | 2020 |
18.1.5. Data source and variables used for derivation and weighting
| Item | Response |
| Data source used for deriving population totals | National business register of the German national statistical office (Destatis) |
| Variables used for weighting | Three different weights are used for qualitative and quantitative variables: - Weights based on number of enterprises: all qualitative variables - Weights based on number of employees: innovation expenditure in NACE B to E, number of employees - Weights based on turnover: innovation expenditure in NACE G, H, J, K, M; turnover with new products, turnover |
18.2. Frequency of data collection
According to the Commission Regulation (UE) 995/2012, the innovation statistics shall be provided to Eurostat every two years in each even year t+18.
In Germany, the innovation survey is conducted every year, and national innovation statistics are produced for each calendar year.
18.3. Data collection
See below
18.3.1. Survey participation
Participation in the survey is voluntary.
18.3.2. Survey type
Stratified random sample survey with a census for enterprises with 500 or more employed persons, combination of paper and online survey.
18.3.3. Combination of sample survey and census data
Combination of both sample survey and census.
18.3.4. Census criteria
500 or more employed persons.
18.3.5. Data collection method
Data collection method
| Survey method | Yes/No | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Face-to-face interview | no | |
| Telephone interview | yes | for non-response survey |
| Postal questionnaire | yes | |
| Electronic questionnaire (format Word or PDF to send back by email) | yes | only in a very few cases if the respondent asked for a pdf version of the questionnaire |
| Web survey (online survey available on the platform via URL) | yes | |
| Other | no |
18.4. Data validation
Not requested.
18.5. Data compilation
Operations performed on data to derive new information according to a given set of rules.
18.5.1. Imputation - rate
Imputation is the method of creating plausible (but artificial) substitute values for all those missing.
Definition of imputation rate:
Imputation rate (for the variable x) (%) = 100*(Number of replaced values) / (Total number of values for a given variable)
Definition of weighted imputation rate:
Weighted imputation rate= 100*(Number of total weighted replaced values) / (Total number of weighted values for a given variable)
18.5.1.1. Imputation rate for metric variables
Imputation rate for metric variables by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 or more persons employed:
| NACE | Size class | Total Turnover (1) | Turnover from products new to the market (2) | R&D expenditure in-house (3) | |||
| Unweighted | Weighted | Unweighted | Weighted | Unweighted | Weighted | ||
| Core NACE (B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73) | Total | 0 | 0 | 17.9 | 55.0 | 11.5 | 17.2 |
| Core industry (B_C_D_E - excluding construction) | Total | 0 | 0 | 17.1 | 38.5 | 12.1 | 8.4 |
| Core Services (46-H-J-K-71-72-73) | Total | 0 | 0 | 19.5 | 57.2 | 10.1 | 18.5 |
(1) = Total turnover in the last year of the reference period (t) (TUR)
(2) = Share of the turnover in the last year of the reference period (t) due to new or improved product new to the market in the total turnover for product innovative enterprises TUR_PRD_NEW_MKT/TUR(INNO_PRD)
(3) = R&D expenditure performed in-house (EXP_INNO_RND_IH)
18.5.2. Weights calculation
Weights calculation method for sample surveys
| Method | Selected applied method | Comments |
| Inverse sampling fraction | yes | |
| Non-respondent adjustments | yes | |
| Other | no |
18.6. Adjustment
No adjustment was applied to the data.
18.6.1. Seasonal adjustment
Not requested.
The Community Innovation Survey (CIS) is a survey about innovation activities in enterprises. The survey is designed to collect the information on types of innovation, processes of development of innovation like cooperation patterns, financing and expenditure, objectives of innovation activities or barriers for initiating or implementing innovation.
The CIS provides statistics by type of innovators, economic activity and size class of enterprises. The survey is currently carried out every two years across the EU Member States, EFTA countries and EU candidate countries.
In order to ensure comparability across countries, Eurostat together with the countries develops a Harmonised Data Collection (HDC) questionnaire and drafts the methodological recommendations for implementation of each survey round.
CIS 2020 is a second in a row to implement concepts and methodology of the Oslo Manual 4th Edition revised in 2018. The changes in the CIS driven by the revision of the manual and their impact on collected indicators are described in the Statistics Explained article: Community Innovation Survey – new features.
The legal framework for CIS since 2012 is the Commission Regulation No 995/2012 that establishes the quality conditions for the data collection and transmission and identifies the obligatory cross-coverage of economic sectors, size class of enterprises and innovation indicators. The target population are enterprises with at least 10 employees classified in the core NACE economic sectors (see 3.3). Further activities may be covered on a voluntary basis in national datasets. Most statistics are based on the 3-year reference period (t, t-1, t-2), but some use only one calendar year (t or t-2). Please refer to the Annex section of the European metadata (ESMS) for details of the time coverage of collected indicators.
28 May 2024
The description of concepts, definitions and main statistical variables is available in CIS 2020 European metadata file (ESMS) Results of the community innovation survey 2020 (CIS2020) (inn_cis12) in Eurostat database.
The statistical unit of the German CIS 2018 is the legal unit according to the definition of legal unit in the Business Register of the Statistical Office of the Federal Republic of Germany.
There are some deviations to this rule in case of large, complex enterprises that are active in different NACE divisions. For some of these large, complex enterprises, the statistical unit is the business unit that best matches the activities of the enterprise that fall under a single NACE division.
Core target population are all enterprises in CORE NACE activities (see 3.3.1) with 10 or more persons employed.
The German CIS 2018 covers all enterprises in the statistical population that are located within the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany.
There is not breakdown of CIS 2018 results by NUTS regions available. The only breakdown available is by Western Germany vs. Eastern Germany.
The microdata nevertheless contain information on the location of an enterprise by NUTS 3-digit level.
For CIS 2020, the time covered by the survey is the 3-year period from the beginning of 2018 to the end of 2020.
Some questions and indicators refer to one year — 2020.
The list of indicators covering the 3-year period and referring to one year according to the HDC is available in the Annex section of the European metadata (ESMS).
Accuracy in the statistical sense denotes the closeness of computations or estimates to the exact or true values. Statistics are not equal with the true values because of variability (the statistics change from implementation to implementation of the survey due to random effects) and bias (the average of the possible values of the statistics from implementation to implementation is not equal to the true value due to systematic effects).
CIS indicators are available according to 3 units of measure:
NR: Number for number of enterprises and number of persons employed.
THS_EUR: Thousands of euros. All financial variables are provided in thousands of euros, i.e. Turnover or Innovation expenditure.
PC: Percentage. The percentage is the ratio between the selected combinations of indicators.
Operations performed on data to derive new information according to a given set of rules.
See below
Differently to the CIS in most other EU member states, the German CIS is conducted every year. Results are therefore published every year. Results of an innovation survey with the reference year t are usually released at the end of January of year t+2.
The timeliness of statistics reflects the length of time between data availability and the event or phenomenon they describe.
The same international standards, concepts and definitions (Oslo manual or Eurostat guidelines) have been applied for all geographical areas of Germany.
Due to important methodological changes driven by Oslo Manual 2018, CIS 2018 and CIS 2020 cannot be directly compared with previous CIS waves.





