Tooth Whiteners & Oral Hygiene Products containing hydrogen peroxide
1. What is hydrogen peroxide and what is it used for?
The SCCP opinion states:
3.OPINION
3.1.Chemical and Physical Specifications
3.1.1.Chemical identity
3.1.1.1. Primary name and/or INCI name
Hydrogen peroxide, dihydrogen dioxide, hydrogen dioxide, hydrogen oxide, oxydol, peroxide.
Carbamide peroxide, urea peroxide, hydrogen peroxide carbamide, urea hydrogen peroxide, urea, compd. with hydrogen peroxide (1:1).
3.1.1.2. Chemical names
3.1.1.3. Trade names and abbreviations
/
3.1.1.4. CAS / EINECS number
Hydrogen peroxide: CAS:7722-84-1
EINECS:231-765-0
Carbamide peroxide: CAS:124-43-6
EINECS:204-701-4
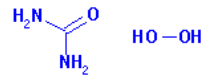
3.1.1.5. Structural formula
3.1.1.6. Empirical formula
Hydrogen peroxide: H2O2
Carbamide peroxide: CO(NH2)2 . H2O2
3.1.2. Physical form
Hydrogen peroxide: Colourless liquid
Carbamide peroxide: White crystals or crystal powder
3.1.3. Molecular weight
Hydrogen peroxide: Mol. weight 34.0
Carbamide peroxide: Mol. weight 94.1
3.1.4. Purity, composition and substance codes
Commercial products:
Hydrogen peroxide: Hydrogen peroxide – water solutions. Commercially supplied as a 33-37% aqueous solution. Common stabilisers include phosphoric or other mineral acid (to keep the product acidic), pyrophosphate salts (complexing agents to inhibit metal-catalysed decomposition) and stannate (a colloid-forming inhibitor).
Commercial solutions contain low (<0.1%) levels of organic impurities (total organic carbon) and very low levels (<10 ppm) of inorganic impurities, with total heavy metals usually <2 ppm. Carbamide peroxide: Products containing minimum 97% of the hydrogen peroxide – Urea adducts are available.
3.1.5.Impurities / accompanying contaminants
/
3.1.6.Solubility
Hydrogen peroxide is miscible with water. Carbamide peroxide is soluble in water.
3.1.7.Partition coefficient (Log Pow)
/
3.1.8.Additional physical and chemical specifications
Pure H2O2 (not commercially available in EU)
Melting point:-0.4°C
Boiling point:150-152°C
Density: 1.4425 g/cm3
Vapour pressure :3 hPa
Melting point:75-85°C
Boiling point:not available
Density:1.4 g/cm3
Vapour pressure : not available
Comment
Possible impurities in hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide are not known. Likewise is the stability of hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide in oral hygiene unknown.
3.2. Function and uses
Hydrogen peroxide is capable of undergoing numerous reactions (e.g., molecular additions, substitutions, oxidations and reductions). It is a strong oxidant and can form free radical by homolytic cleavage. Carbamide peroxide is an adduct of urea and hydrogen peroxide which on contact with water break down to urea and hydrogen peroxide. For example, a 10% carbamide peroxide gel would yield a maximum of 3.6% hydrogen peroxide. 750,000 tonnes hydrogen peroxide (calculated as 100% H2O2) were produced in Europe in 1995. About 300 tonnes of carbamide peroxide were used.
The main usage of hydrogen peroxide is in production of chemicals (approx. 40%), bleaching pulp and paper (approx. 30%) and bleaching textiles (approx. 20%). Small quantities are used in cosmetics. Hydrogen peroxide is used for hair bleaching and for oxidation in permanent hair dyes and in oral hygiene products such as mouth-rinses and dentifrices as well as in tooth bleaching products.
Source & ©: SCCP,
![]()
The Three-Level Structure used to communicate this SCCP Opinion is copyrighted by GreenFacts asbl/vzw