ABC - DEF - GHI - JKL - MNO - PQRS - TUV - WXYZ Alternating current & Direct current
Similar term(s): AC & DC.
Definition:
Alternating Current (AC) is a type of electrical current, in
which the direction of the flow of electrons switches back and forth at regular
intervals or cycles. Current flowing in power lines and normal household
electricity that comes from a wall outlet is alternating current. The standard
current used in the U.S. is 60 cycles per second (i.e. a frequency of 60 Hz); in
Europe and most other parts of the world it is 50 cycles per second (i.e. a
frequency of 50 Hz.).
Direct current (DC) is electrical current which flows
consistently in one direction. The current that flows in a flashlight or another
appliance running on batteries is direct current.
One advantage of alternating current is that it is relatively cheap to change
the voltage of the current. Furthermore, the inevitable loss of energy that
occurs when current is carried over long distances is far smaller with
alternating current than with direct current.
Source: GreenFacts
More:
Graphic representation of the intensity of the current as a function of time:
 Direct current
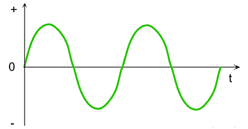 Alternating current
Source: GreenFacts
ABC - DEF - GHI - JKL - MNO - PQRS - TUV - WXYZ |