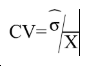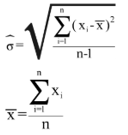|
|
 |
| For any question on data and metadata, please contact: Eurostat user support |
|
|||
| 1.1. Contact organisation | Insee (France) |
||
| 1.2. Contact organisation unit | Direction des statistiques d'entreprises |
||
| 1.5. Contact mail address | Insee Timbre E430 88 avenue Verdier CS 70 058 92 541 Montrouge Cedex |
||
|
|||
| 2.1. Metadata last certified | 01/07/2021 | ||
| 2.2. Metadata last posted | 01/07/2021 | ||
| 2.3. Metadata last update | 01/07/2021 | ||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.1. Data description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Community Innovation Survey (CIS) is a survey about innovation activities in enterprises. The survey is designed to collect the information on different types of innovation, various aspects of the development of an innovation, objectives of innovation activities, sources of information, public funding or expenditure on innovation. It is aim is to measure the innovativeness of sectors and enable the analysis of the factors of innovation. The CIS provides statistics by type of innovators, economic activities and size class of enterprises. The survey is currently carried out every two years across the EU Member States, EFTA countries and EU candidate countries.
In order to ensure comparability across countries, Eurostat together with the countries developed a Harmonised Data Collection (HDC) questionnaire accompanied by a set of definitions and methodological recommendations.
CIS 2018 concepts and its underlying methodology are based on the Oslo Manual (2018) 4th Edition.
New review of the CIS2018 aims to meet several objectives : 1: Reduce subjectivity and biases in the main CIS indicators 2: Improve reporting about innovation activities and capabilities in the firm 3: Ensure international comparability (including compliance with the OM4) 4: Broaden the basis CIS information on enterprise management 5: Take better account the diversity of enterprises in the EU 6: Improve reporting about external drivers and enablers of innovation 7: Improve timeliness 8: Ensure the feasibility of data collection 9: Ensure continuity with the CIS 2016 10: Improve reporting about the output and impact of innovation
CIS2018 is conducted under Commission Regulation No 995/2012. This Regulation defines the mandatory target population of the survey referring to enterprises in the Core NACE economic sectors (see section 3.3.) with at least 10 employees. Further activities may be covered on a voluntary basis in national datasets. Most statistics are based on the 3-year reference period (t, t-1, t-2), but some use only one calendar year (t or t-2).
Please consider CIS t to be the survey that refers to the same year of the quality report and CIS t-2 to be the previous survey e.g.: CIS 2018= CIS t then, CIS t-2=CIS 2016. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.2. Classification system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Indicators related to the enterprises are classified by country, economic activity (NACE Rev. 2), size class of enterprises and type of innovation.
The main typology of classification of enterprises in reference to innovation is the distinction between innovation-active enterprises (INN) and not innovation-active enterprises (NINN). The enterprise is considered as innovative (INN) if during the reference period it successfully introduced a product or business process innovation, had ongoing innovation activities, abandoned innovation activities or was engaged in in-house R&D or R&D contracted out. Non-innovative (NINN) enterprises had no innovation activity mentioned above whatsoever during the reference period. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.3. Coverage - sector | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CIS covers main economic sectors according to NACE Rev.2 broken down by size class of enterprises and type of innovation activity. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.3.1. Main economic sectors covered - NACE Rev.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In accordance with Commission Regulation 995/2012 on innovation statistics, the following industries and services are included in the core target population. Results are made available with these following breakdowns : All NACE – Core NACE (NACE Rev. 2 sections & divisions B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73)
CORE INDUSTRY (excluding construction) (NACE Rev. 2 SECTIONS B_C_D_E) 10-12: Manufacture of food products, beverages and tobacco 13-15: Manufacture of textiles, wearing apparel, leather and related products 16-18: Manufacture of wood, paper, printing and reproduction 20: Manufacture of chemicals and chemical products 21: Manufacture of basic pharmaceutical products and pharmaceutical preparations 19-22: Manufacture of petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, rubber and plastic products 23: Manufacture of other non-metallic mineral products 24: Manufacture of basic metals 25: Manufacture of fabricated metal products, except machinery and equipment 26: Manufacture of computer, electronic and optical products 25-30: Manufacture of fabricated metal products (except machinery and equipment), computer, electronic and optical products, electrical equipment, motor vehicles and other transport equipment 31-33: Manufacture of furniture; jewellery, musical instruments, toys; repair and installation of machinery and equipment
D: ELECTRICITY, GAS, STEAM AND AIR CONDITIONING SUPPLY
E: WATER SUPPLY; SEWERAGE, WASTE MANAGEMENT AND REMEDIATION ACTIVITIES 36: Water collection, treatment and supply 37-39: Sewerage, waste management, remediation activities
CORE SERVICES (NACE Rev. 2 sections & divisions 46-H-J-K-71-72-73)(NACE code in the tables = G46-M73_INN) 46: Wholesale trade, except of motor vehicles and motorcycles
H: TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE 49-51: Land transport and transport via pipelines, water transport and air transport 52-53: Warehousing and support activities for transportation and postal and courier activities
J: INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION 58: Publishing activities 61: Telecommunications 62: Computer programming, consultancy and related activities 63: Information service activities
K: FINANCIAL AND INSURANCE ACTIVITIES 64: Financial service activities, except insurance and pension funding 65: Insurance, reinsurance and pension funding, except compulsory social security 66: Activities auxiliary to financial services and insurance activities
M: PROFESSIONAL, SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL ACTIVITIES 71: Architectural and engineering activities; technical testing and analysis 72: Scientific research and development 73: Advertising and market research 71-73: Architectural and engineering activities; technical testing and analysis; Scientific research and development; Advertising and market research |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.3.1.1. Main economic sectors covered - NACE Rev.2 - national particularities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The enterprises belonging to divisions 05 to 81 of NACE Rev. 2 (with the exception of 75: Veterinarians). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.3.2. Sector coverage - size class | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In accordance with Commission Regulation 995/2012 on innovation statistics, the following size classes of enterprises according to number of employees are included in the core target population of the CIS:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.3.2.1. Sector coverage - size class - national particularities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There were 4 size classes : the size class 10-49 employees was broken down into two subclasses, the enterprises of 10-19 employees and the enterprises of 20-49 employees. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.4. Statistical concepts and definitions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The description of concepts, definitions and main statistical variables is available in CIS 2018 European metadata file (ESMS) Results of the community innovation survey 2018 (CIS2018) (inn_cis11) in Eurostat database. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.5. Statistical unit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The responding unit is the legal unit, identified by its SIREN number, with the exception of 12 units which are interviewed as profiled companies. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.6. Statistical population | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Core target population are all enterprises in CORE NACE activities (see 3.3.1) with 10 or more employees. More specifically, for the French survey, the legal units surveyed are units located in France (metropolitan France and the French overseas departments, including Mayotte), active as of 31/12/2018 and having had at least 6 months of activity, merchants, operators with 10 or more employees (in FTEs) excluding the Syndicat Intercommunal à Vocation Unique (SIVU) (legal category 7353). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.7. Reference area | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Metropolitan France and overseas departments including Mayotte. CIS data are available by region. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.8. Coverage - Time | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Several rounds of Community Innovation Survey have been conducted so far at two-year interval since end of 90’s. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.8.1. Participation in the CIS waves | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
*two reference periods can be distinguished for CIS light: 2000-2002 and 2001-2003 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.9. Base period | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not relevant. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||
CIS indicators are available according to 3 units of measure:
NR: Number for number of enterprises and number of persons employed. THS_EUR: Thousands of euros. All financial variables are provided in thousands of euros, i.e. Turnover or Innovation expenditure. PC: Percentage. The percentage is the ratio between the selected combinations of indicators. |
|||
|
|||
For CIS 2018, the time covered by the survey is the 3-year period from the beginning of 2016 to the end of 2018. Some questions and indicators refer to one year — 2018. The list of indicators covering the 3-year period and referring to one year according to the HDC is available in the Annex section of the European metadata (ESMS). |
|||
|
|||
| 6.1. Institutional Mandate - legal acts and other agreements | |||
CIS surveys are based on the Commission Regulation No 995/2012, implementing Decision No 1608/2003/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the production and development of Community statistics on science and technology. This Regulation establishes innovation statistics on a statutory basis and makes the delivery of certain variables compulsory e.g. innovation activities, cooperation, development, expenditures and turnover (see the Regulation). Each survey wave may additionally include further variables. In addition, the Regulation defines the obligatory cross-coverage of economic sectors and size class of enterprises. |
|||
| 6.1.1. National legislation | |||
At the national level, the committees that gave INSEE the right and legitimacy to collect this data are:
|
|||
| 6.2. Institutional Mandate - data sharing | |||
Not requested. |
|||
|
|||
CIS data are transmitted to Eurostat via EDAMIS using the secured transmission system. |
|||
| 7.1. Confidentiality - policy | |||
Statistical confidentiality applied for the data set in question. |
|||
| 7.2. Confidentiality - data treatment | |||
The data disseminated respects statistical confidentiality rules. Primary confidentiality : No cell of the table may concern less than three units. No cell of the table may contain data for which a company represents more than 85 % of the total. Secondary confidentiality is treated with the tool Tau-Argus. |
|||
|
|||
| 8.1. Release calendar | |||
For Eurostat, the first results are send at the end of June 2020. The first French publication of the results was on August 25th, 2020. The micro-data are made available to users at the end of 2020, after passing through the secrecy committee. Access to the secure data center is required to use them.
This calendar is similar from one CIS survey to another, but is not publicly available. |
|||
| 8.2. Release calendar access | |||
Not relevant. |
|||
| 8.3. Release policy - user access | |||
The micro-data are made available to users, after passing through the secrecy committee. Access to the secure data center is required to use them. |
|||
|
|||
CIS is conducted and disseminated at two-year interval in pair years. |
|||
|
|||||||||||||||
Accessibility and clarity refer to the simplicity and ease for users to access statistics using simple and user-friendly procedure, obtaining them in an expected form and within an acceptable time period, with the appropriate user information and assistance: a global context which finally enables them to make optimum use of the statistics. |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.1. Dissemination format - News release | |||||||||||||||
See below. |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.1.1. Availability of the releases | |||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| 10.2. Dissemination format - Publications | |||||||||||||||
- Online database (containing all/most results) : Yes The database is avaible to researchers who ask to have access. Their formal request is analysed before they have access to the database. The access is granted via Insee’s CASD (Centre d’Accès Securisé aux Données) which is a highly secured environment for remote access to databases. It’s similar to the SAFE Center security-wise, but without having distant access (access requires login and password).
- Analytical publication (referring to all/most results) : Yes The national publication is a 4 pages electronic release (Insee Première). However, paper releases are minimal, in favour of the electronic format.
- Analytical publication (referring to specific results, e.g. only for one sector or one specific aspect) : Yes Insee Référence Entreprises - Short statistical results |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.3. Dissemination format - online database | |||||||||||||||
The database is avaible to researchers who ask to have access. Their formal request is analysed before they have access to the database. The access is granted via Insees CASD (Centre dAccs Securis aux Donnes) which is a highly secured environment for remote access to databases. Its similar to the SAFE Center security-wise, but without having distant access (access requires login and password). |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.3.1. Data tables - consultations | |||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.4. Dissemination format - microdata access | |||||||||||||||
The micro-data are made available to users, after passing through the secrecy committee. Access to the secure data center is required to use them. |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.4.1. Dissemination of microdata | |||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| 10.5. Dissemination format - other | |||||||||||||||
No other data dissemination. |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.5.1. Metadata - consultations | |||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.6. Documentation on methodology | |||||||||||||||
We publish also on INSEE website a dictionary of variables and a quality report that describes briefly each step of implemeting CIS2018 survey. The CIS microdata delivered via the French CASD comes with the CIS questionnaire, a dictionnary of variables, the european 995/2012 reglementation, sample design documentation and a quality report (different to the Eurostat Quality Report). https://www.insee.fr/en/metadonnees/source/operation/s1477/presentation |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.6.1. Metadata completeness - rate | |||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
|||||||||||||||
| 10.7. Quality management - documentation | |||||||||||||||
A short quality report is published on the INSEE website. https://www.insee.fr/en/metadonnees/source/operation/s1477/presentation |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||
| 11.1. Quality assurance | |||
The different steps of the survey ensure that the process meets the requirements for statistical production: |
|||
| 11.2. Quality management - assessment | |||
Model questionnaire is translated to produce the national questionnaire. Methodological Manual guidelines are also used. Processing is carried out during and after collection data in order to guarantee the best possible quality of the results: responses to respondents' questions, implementation of controls, checks on the consistency of the controls and post-collection processing to correct non-response. However, Variables with high partial non-response rates should be interpreted with caution, since a non-negligible part of their responses has been imputed. These include the following variables (from 5% to 31% partial non-response, with variables listed by decreasing partial non-response rate): EXPDESIGN, EXPDPI, EXPSFTW, EXEXPPCT, RMACX, RSERVX, REMPX, EXPMKT, EXPTRAIN, ROTRX, TURNIN, TURNMAR, EXPMAC, TURNNEW, RRDINX, EXAEXP, RRDEXX, and some variables on the type of cooperation partners for innovation activities. |
|||
|
||||||||||||||||||
Relevance is the degree to which statistics meet current and potential users needs. It includes the production of all needed statistics and the extent to which concepts used (definitions, classifications etc.) reflect user needs. The aim is to describe the extent to which the statistics are useful to, and used by, the broadest array of users. For this purpose, statisticians need to compile information, firstly about their users and their needs. The CIS is based on a common questionnaire and a common survey methodology, as laid down in the 3rd edition of Oslo Manual (2005 edition), in order to achieve comparable, harmonised and high quality results for EU Member States, EFTA countries, Candidates and Associated countries. |
||||||||||||||||||
| 12.1. Relevance - User Needs | ||||||||||||||||||
Insee answers to users needs as much as possible. One year before data collection, the meeting is held with innovation specialists, to gather the consideration and ideas and possible requests on questions to add. People who attend the meetings are from relevant ministries (Higher Education & Research, Transport, Industry etc.), researchers, social actors. The methodologists and data collection experts also attend the meeting. |
||||||||||||||||||
| 12.1.1. Needs at national level | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| 12.2. Relevance - User Satisfaction | ||||||||||||||||||
A satisfaction survey was conducted among those who clicked on the link of the internet publication. The collection began on the day the publication was published on the INSEE website and lasted fifteen days. The 160 respondents are globally satisfied with the publications. |
||||||||||||||||||
| 12.3. Completeness | ||||||||||||||||||
All the mandatory sectors of Nace Rev. 2 and questions were surveyed for CIS2018. Some Eurostat optional questions were removed from the French questionnaire : - Question 2.4 (percentage of turnover in 2018 from products resulting from 'customisation' or 'co-creation', and standardised products) - Question 2.11 (importance of methods of organising work in the management) - Question 3.11 (2020 compared to 2019) |
||||||||||||||||||
| 12.3.1. Data completeness - rate | ||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.1. Accuracy - overall | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accuracy in the statistical sense denotes the closeness of computations or estimates to the exact or true values. Statistics are not equal with the true values because of variability (the statistics change from implementation to implementation of the survey due to random effects) and bias (the average of the possible values of the statistics from implementation to implementation is not equal to the true value due to systematic effects). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.2. Sampling error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
That part of the difference between a population value and an estimate thereof, derived from a random sample, which is due to the fact that only a subset of the population is enumerated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.2.1. Sampling error - indicators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The main indicator used to measure sampling errors for CIS data is the coefficient of variation (CV).
Coefficient of Variation= (Square root of the estimate of the sampling variance) / (Estimated value) Formula: where
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.2.1.1. Coefficient of variations for key variables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coefficient of variation (%) for key variables by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 and more employees
[1] = Coefficient of variation for the percentage of innovative enterprises (INN) in the total population of enterprises (ENT18) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.2.1.2. Variance estimation method | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
To measure variance estimation, weighting and the sample design have been taken into account. We divided the estimated standard deviation by the estimated average for each of the variables requested, in order to determinate the coefficient of variation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3. Non-sampling error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-sampling errors occur in all phases of a survey. They add to the sampling errors (if present) and contribute to decreasing overall accuracy. It is important to assess their relative weight in the total error and devote appropriate resources for their control and assessment. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1. Coverage error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coverage errors (or frame errors) are due to divergences between the target population and the frame population. The frame population is the set of target population members that has a chance to be selected into the survey sample. It is a listing of all items in the population from which the sample is drawn that contains contact details as well as sufficient information to perform stratification and sampling. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1.1. Over-coverage - rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1.2. Common units - proportion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1.3. Under covered groups of the target population | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Like with the business registrer SIRENE, information on legal units which ceased their activity are not integrated in real-time. Entreprises are active on 31/12/2018 but there may be some cessations were recorded after the date of sampling. As a consequence, several units could have been included wrongly in the sample. Moreover, for the sampling, the size of a unit is determined by the number of full-time employees and is a provisional size from 2017 if it is available. If not we took the 2016 final size. For the enterprises born after 31/12/2017, we took the number of employees declared at the creation even if it’s not the number of full-time employees. For those created before 31/12/2015 and for which we do not have any size, we classified them as out of scope. The size of some units changed, and could fall below the threshold of 10 employees. These units, are however kept in the sample. Enterprises that reported having fewer than 10 employees are theoretically out of scope. However, they are partially kept in the sample in order to represent enterprises that are not in the survey frame even though their workforce has increased recently. The rule for enterprises reporting fewer than 10 employees is as follows: - those that reported having less than 4 employees are excluded - those which reported having between 5 and 9 employees and whose number of employees at the time of the sample draw was greater than 20 are excluded. A large variation in the number of employees implies a different profile. - those which reported having between 5 and 9 employees and whose number of employees at the time of the sample draw was less than 20 are kept in the sample. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1.4. Coverage errors in coefficient variation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The CVs reported do not incorporate the effects of coverage errors. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.2. Measurement error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Measurement errors occur during data collection and generate bias by recording values different than the true ones. The survey questionnaire used for data collection may have led to the recording of wrong values, or there may be respondent or interviewer bias. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.2.1. Measures for reducing measurement errors | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The CIS 2018 questionnaire was tested after its finalization by Eurostat, almost one year before the start of data collection. The results of these tests allowed for feedback from enterprises on this new questionnaire, and to ensure that it was well understood. They were also useful for obtaining the visa for french CIS. In addition, in order to ensure proper data collection, the survey managers (gestionnaires) were trained a few days before the start of the survey. The training provided an overview of the CIS survey and addressed each question in detail. Survey managers are used for business surveys and are trained for this purpose. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3. Non response error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non response occurs when a survey fails to collect data on all survey variables from all the population units designated for data collection in a sample or complete enumeration. There are two types of non-response: 1) Unit non-response, which occurs when no data (or so little as to be unusable) are collected about a population unit designated for data collection. a) Un-weighted unit non-response rate (%) = 100*(Number of units with no response or not usable response) / (Total number of in-scope (eligible) units in the sample) b) Weighted unit non-response rate (%) = 100*(Number of weighted units with no response or not usable response) / (Total number of in-scope (eligible) units in the sample) 2) Item non-response, which occurs when only data on some, but not all survey data items are collected about a population unit designated for data collection. a) Un-weighted item non-response rate (%) = 100*(Number of units with no response at all for the item) / (Total number of eligible, for the item, units in the sample i.e. filters have to be taken into account) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1. Unit non-response - rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See below. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1.1. Un-weighted and weighted unit non-response rate by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 or more employees | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Un-weighted and weighted unit non-response rate by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 or more employees
The number of eligible units is the number of sample units, which indeed belong to the target population. We have removed from the calculation the units finally put out of scope. For the weighted unit non-response rate, we used the launch weight because once enterprises declared non-respondant we calcule all the weights to adjust the data and the non-response unit do not have a weight anymore. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1.2. Maximum number of recalls/reminders before coding | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For the French CIS 2018 survey, an enterprise is coded as non-responding after 3 reminders. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.2. Item non-response - rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See below. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.2.1. Item non-response rate for Turnover (in Core NACE: B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73 enterprises with 10 or more employees) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Item non-response rate for Turnover (in Core NACE: B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73 enterprises with 10 or more employees).
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.2.2. Item non response rate for new questions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Item non-response rate for new questions in CIS t (in Core NACE: B-C-D-E-46-H-J-K-71-72-73 enterprises with 10 or more employees)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.4. Processing error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There are no processing errors. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.5. Model assumption error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||
Timeliness and punctuality refer to time and dates, but in a different manner. |
|||
| 14.1. Timeliness | |||
The timeliness of statistics reflects the length of time between data availability and the event or phenomenon they describe. |
|||
| 14.1.1. Time lag - first result | |||
Timeliness of national data – date of first release of national level : August 25th, 2020 |
|||
| 14.1.2. Time lag - final result | |||
Not requested. |
|||
| 14.2. Punctuality | |||
Punctuality refers to the time lag between the release date of data and the target date on which they were scheduled for release as announced officially. |
|||
| 14.2.1. Punctuality - delivery and publication | |||
Date of transmission of complete and validated data to Eurostat (Number of days between that data and 30 June 2020) : 0 |
|||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Comparability aims at measuring the impact of differences in applied statistical concepts and definitions on the comparison of statistics between geographical areas, non-geographical domains, or over time. The coherence of statistical outputs refers to the degree to which the statistical processes by which they were generated used the same concepts (classifications, definitions, and target populations) and harmonised methods. Coherent statistical outputs have the potential to be validly combined and used jointly. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.1. Comparability - geographical | ||||||||||||||||||||
To meet the representativeness criteria of Euopean constraints we have been adding the regions in the survey design since CIS 2016. If the number of units in the drawn stratum was big enough we used a88*size*region to stratify, otherwise we used simply a88*size. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.1.1. Asymmetry for mirror flow statistics - coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.1.2. National questionnaire – compliance with Eurostat model questionnaire | ||||||||||||||||||||
Methodological deviations from the CIS Harmonised Data Collection (HDC)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.1.3. National questionnaire – additional questions | ||||||||||||||||||||
Methodological deviations from the CIS Harmonised Data Collection (HDC)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.2. Comparability - over time | ||||||||||||||||||||
Due to important methodological changes in CIS 2018 driven by Oslo Manual 2018, the data 2018 cannot be directly compared with previous CIS waves. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.2.1. Length of comparable time series | ||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.3. Coherence - cross domain | ||||||||||||||||||||
See the comparison between SBS and CIS data in the section 15.3.3 below. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.3.1. Coherence - sub annual and annual statistics | ||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.3.2. Coherence - National Accounts | ||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.3.3. Coherence – Structural Business Statistics (SBS) | ||||||||||||||||||||
This part compares key variables for aggregated CIS data with SBS data
* Numbers are to be provided for the last year of the reference period (t) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.4. Coherence - internal | ||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||
Confidential information on the production cost of the CIS. |
|||
|
|||
| 17.1. Data revision - policy | |||
Not requested. |
|||
| 17.2. Data revision - practice | |||
Not requested. |
|||
| 17.2.1. Data revision - average size | |||
Not requested. |
|||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.1. Source data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See below: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.1.1. Sampling frame (or census frame) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The frame was built mainly from the french statistical business register SIRUS, the annual statistics on entreprises (ESANE), the annual sectorial survey (ESA) and the annual production survey (EAP). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.1.2. Sampling design | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The sample is drawn from a sampling frame constructed from the Sirus inventory using a simple random sampling design stratified by activity, size classes, region and the notion of belonging to a group (and its French or foreign status) where possible. The calculation of the allocations combines a Neyman allocation on the rate of innovative units and a proportional allocation on the number of innovative units, which makes it possible on the one hand to be precise on the central variable of the survey (the innovation rate) and also to query a reasonable number of innovative units in order to ensure satisfactory accuracy for questions concerning only these units. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.1.3. Target population and sample size | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.1.4. Data source for pre-filled variables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Variables and indicators filled or prefilled from other sources.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.1.5. Data source and variables used for derivation and weighting | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.2. Frequency of data collection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
According to the Commission Regulation (UE) 995/2012, the innovation statistics shall be provided to Eurostat every two years in each even year. The data collection takes place every second year in year t-2 preceding the data provision. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.3. Data collection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See below. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.3.1. Survey participation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The survey is mandatory. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.3.2. Survey type | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Collection of data was realized through a combination of sampling and census. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.3.3. Combination of sample survey and census data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A sample survey was used to collect data for the enterprises of less than 250 employees. For census criteria, see 18.3.4. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.3.4. Census criteria | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A sample survey was used to collect data for the enterprises of less than 250 employees. Census is used for entreprises of 250 employees or more and for enterprises with less than 250 employees but validating at least one of these 3 criteria (23% of the sample):
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.3.5. Data collection method | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data collection method
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.4. Data validation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.5. Data compilation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operations performed on data to derive new information according to a given set of rules. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.5.1. Imputation - rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Imputation is the method of creating plausible (but artificial) substitute values for all those missing. Definition of imputation rate: Imputation rate (for the variable x) (%) = 100*(Number of replaced values) / (Total number of values for a given variable) Definition of weighted imputation rate: Weighted imputation rate= 100*(Number of total weighted replaced values) / (Total number of weighted values for a given variable) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.5.1.1. Imputation rate for metric variables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Imputation rate for metric variables by NACE categories and for enterprises with 10 or more employees:
(1) = Total turnover in the last year of the reference period (t) (TUR) (2) = Share of the turnover in the last year of the reference period (t) due to new or improved product new to the market in the total turnover for product innovative enterprises TUR_PRD_NEW_MKT/TUR(INNO_PRD) (3) = R&D expenditure performed in-house (EXP_INNO_RND_IH) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.5.2. Weights calculation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Weights calculation method for sample surveys
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.6. Adjustment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The final weights result from the sampling design, correction of total non-response, calibration on auxiliary data and winsorisation (impact reduction of atypical data). The method of response homogeneity groups has been used to reflect in the weights the behavior of non-response of certain strata of units. Then, data have been calibrated with CALMAR 2, at a level of crossing activity (A38 level) and size. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18.6.1. Seasonal adjustment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||