|
|
 |
|
| For any question on data and metadata, please contact: Eurostat user support |
|
|||
| 1.1. Contact organisation | Croatian Institute of Public Health |
||
| 1.2. Contact organisation unit | Public Health Service, Department for Health Economics |
||
| 1.5. Contact mail address | Rockfellerova 7 HR-10000 Zagreb
|
||
|
|||
| 2.1. Data description | |||
Health care expenditure quantifies the economic resources dedicated to health functions, excluding capital investment. Healthcare expenditure concerns itself primarily with healthcare goods and services that are consumed by resident units, irrespective of where that consumption takes place (it may be in the rest of the world) or who is paying for it. As such, exports of healthcare goods and services (to non-resident units) are excluded, whereas imports of healthcare goods and services for final use are included. It provides a set of revised classifications of health care functions, providers of health care goods and services and financing schemes. The SHA is currently used as a basis for a joint data collection by OECD, Eurostat and WHO on health care expenditure. The manual sets out in more detail the boundaries, the definitions and the concepts of health accounting – responding to health care systems around the globe with very different organisational and financing arrangements. Accounting period: Health expenditure and financing data pertain to the calendar year (1 January to 31 December). Croatian Institute of Public Health (CIPH) is compiling SHA data on the basis of the Official Statitics Act, Programme of Statitical Activities and Annual Implementation Plan of Statistical Activities of the Republic of Croatia. |
|||
| 2.2. Classification system | |||
Healthcare expenditure is recorded in relation to the international classification for health accounts (ICHA) defining:
|
|||
| 2.3. Coverage - sector | |||
1. Household individual consumption on health, including the collective consumption with two exceptions: |
|||
| 2.4. Statistical concepts and definitions | |||
SHA concept is the consumption of health care goods and services. Summary tables provide data on:
Cross-classification tables refer to:
|
|||
| 2.5. Statistical unit | |||
Commission Regulation 2015/359 concerns the collection of data on "current expenditure on healthcare" which is defined as the "final consumption expenditure of resident units on health care goods and services". |
|||
| 2.6. Statistical population | |||
SHA focuses on the consumption of health care goods and services by the resident population irrespective of where this takes place. This implies the inclusion of imports (from non-resident providers) and the exclusion of exports (health care goods and services provided to non-residents). |
|||
| 2.7. Reference area | |||
The data aims at providing a complete overview of expenditure on health care goods and services consumption of services and goods by the resident population on the national territory of a country. |
|||
| 2.8. Coverage - Time | |||
2013-2016. |
|||
| 2.9. Base period | |||
Not applicable. |
|||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.1. Source data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Several data sources are used (as of data notification in March 2018): - Surveys/census: 1 - Public administrative records: 9 - Financial reports: 3 - Other: 1
Surveys/censuses
Public administrative records
Financial reports
Other
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.2. Frequency of data collection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Annual. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.3. Data collection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data are collected through the joint health accounts questionnaire (JHAQ) that countries submit to Eurostat during the annual data collection exercise. There is a voluntary deadline to send the JHAQ questionnaire for the calendar year T by the 31st of March T+2. The joint health accounts questionnaire (JHAQ) is coordinated in agreement with the World Health Organisation (WHO) and the Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). These three international organisations are known collectively as the International Health Accounts Team (IHAT). Countries submit data to Eurostat on the basis of Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/359 of 4 March 2015 implementing Regulation (EC) No 1338/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards statistics on healthcare expenditure and financing. Majority of the data from social insurance fund is transmitted in standardised electronic form containing data compiled according to mapping of different internal social insurance fund's code books into SHA categories which is prepared and provided by Croatian Institute of Public Health. The remaining data from social insurance fund are transmitted in non-standardised form and procesed and SHA coded by Croatian Institute of Public Health. The data from other reporting units (financing agents) which use public administrative records are transmitted in standardised electronic form, while data from survey and financial reports are processed and SHA coded by Croatian Institute of Public Health. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.4. Data validation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2018 JHAQ includes a number of features which allow national data correspondents to perform various quality checks before submitting the data. The embedded programmes allow the verification of:
2- Consistency of the data within tables,
Entries in the tables cannot be negative as they refer to the consumption of goods and services.
The atypical entries check provides information whether the data tables contain values in cells which are – if at all – only reported by very few countries and are thus atypical for health accounting.
3- The growth rates against the previous year and the magnitude of revisions as compared to previously submitted data. Results are grouped into three different categories:
Croatian Institute of Public Health also provides national data validation - manual validation is performed throughout the compilation process: - evaluation of completeness and coverage of each data source - control and analysis of microdata received from each reporting unit - analysis of time series for each data source - cross checking between SHA data and other published data and reports on health care expenditures. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.5. Data compilation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SHA data is compiled both by a bottom-up approach as well as by a top-down approach, depending on the data source. Compilation is done by financing schemes and by different health care functions/task areas. The results of the several calculations are then aggregated. To gain the differentiation between the different SHA-dimensions (especially HC and HP) quotas and pro-rating and utilisation keys are applied on some spending items. For some spending items it is necessary to extra-/intrapolate data as there is no up-to-date data available or data is missing for certain years. For some other spending items, estimation methods have to be applied.
Several methods are normally used for estimations:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.6. Adjustment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not applicable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||
| 4.1. Quality assurance | |||
Authorities responsible for SHA data collection are working to ensure that the statistical practices used to compile national health accounts are in compliance with SHA methodological requirements and that good practices in the field are being followed, according to the methodology underlined in the SHA 2011 Manual and European Statistics Code of Practice respecting professional independence of the statistical authorities. Procedures are in place to plan and monitor the quality of the health care expenditure statistical production process. |
|||
| 4.2. Quality management - assessment | |||
The majority of SHA data for Croatia are collected using "bottom-up" approach - individual data from administrative data sources are collected and compiled according to SHA methodology. The main source of data where this approach is not applied is Household Budget Survey which is source of majority of data for HF.3. As Household Budget Survey is executed in Croatia only every third year (2011, 2014, 2017), data for 2015 and 2016 had to be estimated from data for 2014. Besides that, questions in Household Budget Survey are not adapted to SHA methodology, so estimations are needed to obtain data according to SHA methodology. Due to all mentioned reasons, SHA data on HF.3 derived from Household Budget Survey are considered to be of lower quality and less reliable compared to the remaining SHA data. |
|||
|
|||
| 5.1. Relevance - User Needs | |||
Data users at the national level are Ministry of Health as well as researchers and analysts in the area of health care. |
|||
| 5.2. Relevance - User Satisfaction | |||
Croatian Institute of Public Health has regular contacts with Ministry of Health which has opportunity to give its opinion from the user point of view. |
|||
| 5.3. Completeness | |||
The breakdown of HF.3 into HF.3.1 ("Out-of-pocket excluding cost-sharing") and HF.3.2 ("Cost-sharing with third-party payers") is not available. |
|||
| 5.3.1. Data completeness - rate | |||
Not available. |
|||
|
|||
| 6.1. Accuracy - overall | |||
The overall accuracy of SHA data depends on the accuracy of the data used to compile them. In general, data derived from administrative data sources are more accurate, while the data from Household Budget Survey and financial reports which undergo significant tranformations before inclusion into SHA data, are less accurate. |
|||
| 6.2. Sampling error | |||
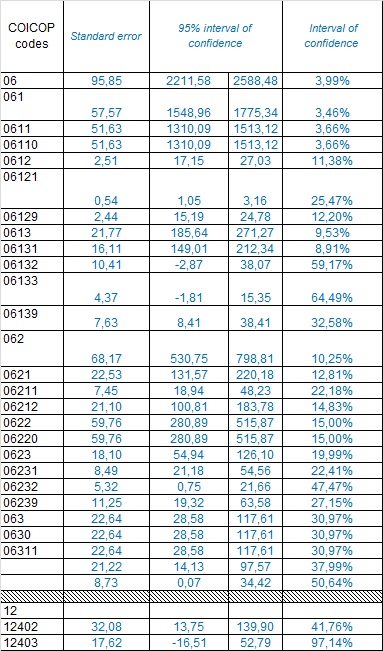
Household Budget Survey is used as the main source of data for HF.3 expenditures. Sampling error indicators for data categories from Household Budget Survey (according to their COICOP codes) which are used for SHA data compilation, are presented in the following table:
|
|||
| 6.2.1. Sampling error - indicators | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3. Non-sampling error | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3.1. Coverage error | |||
We are not aware of any double-counting of expenditure items in SHA data. However, we are countinouosly checking our data for possible double-counting and in any such case we do revision of complete time series of the data (we had such case last year when we discovered that certain expenditure reported by social insurance fund as final consumption was actually internal transfer from voluntary to mandatory health insurance section within the social insurance fund - we immediately asked for corrected data and did revision of the complete time series of SHA data). Health care goods and services by non-residents are excluded . We are not able to report the underground/informal/illegal health care goods and services (Croatian Bureau of Statistics who operates Household Budget Survey in Croatia provided us with information that informal payments are not included in data collected as part of this survey which is our main source for HF.3). |
|||
| 6.3.1.1. Over-coverage - rate | |||
None. |
|||
| 6.3.1.2. Common units - proportion | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3.2. Measurement error | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3.3. Non response error | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3.3.1. Unit non-response - rate | |||
Stated in metadata according to HF categories. |
|||
| 6.3.3.2. Item non-response - rate | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3.4. Processing error | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3.4.1. Imputation - rate | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.3.5. Model assumption error | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 6.4. Seasonal adjustment | |||
Not applicable. |
|||
| 6.5. Data revision - policy | |||
SHA data undergo revision whenever new or corrected data on certain health care expenditure become available for a certain year. One of the main problems with SHA data is still the fact that health care providers owned by the state (mostly hospitals) accumulate losses which get covered only several years after they were generated and which can not be so precisely devided into HC categories as it is possible for expenditures which actually get paid (therefore estimations are needed). |
|||
| 6.6. Data revision - practice | |||
Revised data for 2013, 2014, 2015 and 2016 are included in submission in 2018. There has been intensive correspondence with Croatian Health Insurance Fund (providing HF.1.2.1 and big part of HF.2.1) concerning problems with huge variations in HC.5.1.1 among different years (mentioned in point 8. of your validation) without knowing the reasons. This resulted in series of meetings and intensive mail correspondence during which several methodological problems have been discovered (limited not only to HC.5.1.1) in reporting of SHA data from Croatian Health Insurance Fund, therefore revised data for entire period 2013-2016 has been requested. The revisions included significant changes in HC.5.1.1, HC.1.3.1, HC.1.3.2, HC.1.4, HC.3.4, HC.5.1.3 and HC.6. Additional revision of data for 2013-2016 included in submission in 2019: Source for expenditures in HF.3 HC.5.1.1. and HF. 3 HC.5.1.2 was changed - instead of Household Budget Survey data we decided to use data from the report on drug utilisation in Croatia prepared by Agency for Medicinal Products and Medical Devices of Croatia as their data are more accurate. |
|||
| 6.6.1. Data revision - average size | |||
Not available. |
|||
|
|||
| 7.1. Timeliness | |||
Croatia transmits its data to Eurostat in compliance with the Commission Regulation 359/2015 transmission deadlines. |
|||
| 7.1.1. Time lag - first result | |||
Provisional results are published in May T+2. |
|||
| 7.1.2. Time lag - final result | |||
Final results are published in October/November T+2 (after completion of Eurostat validation). Revised results are published after each revision of the data. |
|||
| 7.2. Punctuality | |||
Croatia complies with Commission Regulation 359/2015 transmission deadlines. |
|||
| 7.2.1. Punctuality - delivery and publication | |||
Croatia delivers the data for T-2 to Eurostat by 30th March T. |
|||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.1. Comparability - geographical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not applicable at national level. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.1.1. Asymmetry for mirror flow statistics - coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not applicable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.2. Comparability - over time | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Breaks in time series resulting from methodological changes
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.2.1. Length of comparable time series | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2013-2017 for SHA 2011 data. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.3. Coherence - cross domain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SHA and ESSPROS data (managed by Croatian Bureau of Statistics) are regularly compared (although they are compiled by different institutions using different methodologies) and checked for any differences which can not be explained by differences in SHA and ESSPROS methodology. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.4. Coherence - sub annual and annual statistics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not applicable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.5. Coherence - National Accounts | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Does not exist for the time being. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.6. Coherence - internal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Atypical entries:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||
| 9.1. Dissemination format - News release | |||
Preliminary SHA data for T-2 are regularly published in May each year on internet site of Croatian Institute of Public Health. |
|||
| 9.2. Dissemination format - Publications | |||
SHA data for Croatia are regularly published in Croatian Health Statistics Yearbook (yearbook for 2017 available on the link: https://www.hzjz.hr/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/Ljetopis_2017.pdf (SHA data published in the statistical yearbook are NOT replaced after revisions). SHA data for Croatia are also regularly published in annual SHA reports (last available is report for 2016 available on the link: https://www.hzjz.hr/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Bilten_SHA_2016_v_2_sije_2019.pdf ). Whenever there is a revision of SHA data for certain year, new SHA report with SHA data for that year is prepared and published (with "revised data" label). |
|||
| 9.3. Dissemination format - online database | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 9.3.1. Data tables - consultations | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 9.4. Dissemination format - microdata access | |||
Not applicable. |
|||
| 9.5. Dissemination format - other | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 9.6. Documentation on methodology | |||
Methodology is described in a special paragraph on methodology in the annual SHA report. |
|||
| 9.7. Quality management - documentation | |||
There are no official documents concerning quality management of SHA data. |
|||
| 9.7.1. Metadata completeness - rate | |||
Not available. |
|||
| 9.7.2. Metadata - consultations | |||
Not available. |
|||
|
|||
| Restricted from publication | |||
|
|||
| 11.1. Confidentiality - policy | |||
The Regulation (EC) No 223/2009 on European statistics (recitals 23-27, 31-32 and Articles 20-26) applies. The Official Statistics Act which regulates production and dissemination of SHA data in Croatia also obliges Croatian Institute of Public Health to keep data collected from reporting units confidential and to publish only aggregated SHA data. |
|||
| 11.2. Confidentiality - data treatment | |||
Collected data are kept confidential as required by regulations and only aggregated data are published. |
|||
|
|||
No further comments. |
|||
|
|||
|
|||