4.2 How efficient are we in our consumption of energy?
One of the priorities of the Energy Union strategy is to increase energy efficiency in an attempt to reduce energy consumption by 20 % by 2020.
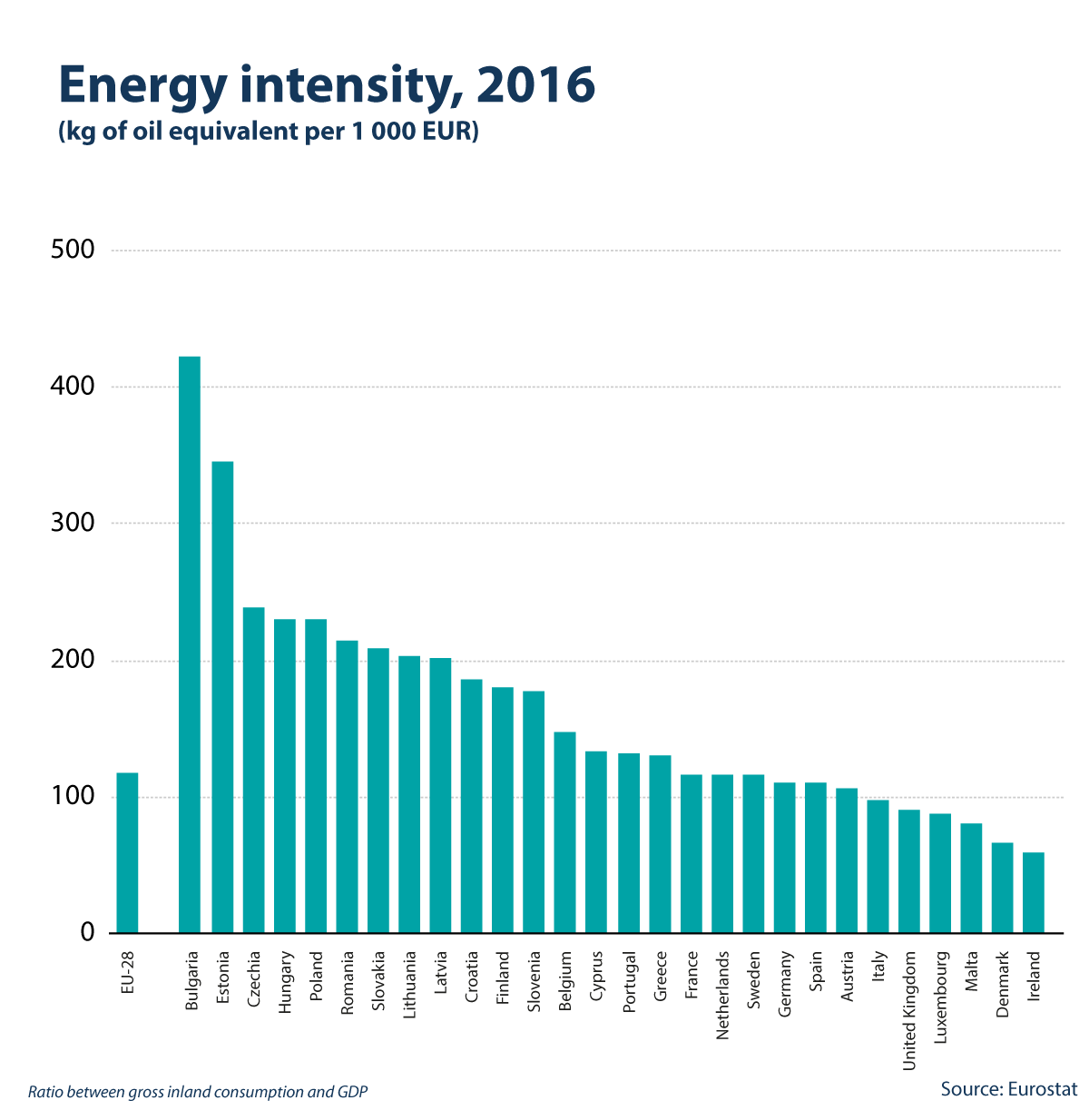
Energy intensity is a measure of an economy’s energy efficiency and shows how much energy is needed in order to produce a unit of gross domestic product (GDP). For instance, if an economy becomes more efficient in its use of energy and its GDP remains constant, then the ratio for this indicator should fall. It is expressed in kilograms of oil equivalent per EUR 1 000 of GDP.
The least intensive economies in the EU in 2016, i.e. those using the least amount of energy relative to their overall economic size (based on GDP), were Ireland, Denmark, Malta, Luxembourg and the United Kingdom. The most energy-intensive EU Member States were Bulgaria and Estonia. It should be noted that the economic structure of a country plays an important role in determining energy intensity, as service based economies will, a priori, display relatively low energy intensities, while economies with heavy industries (such as iron and steel production) may have a considerable proportion of their economic activity within industrial sectors, thus leading to higher energy intensity.